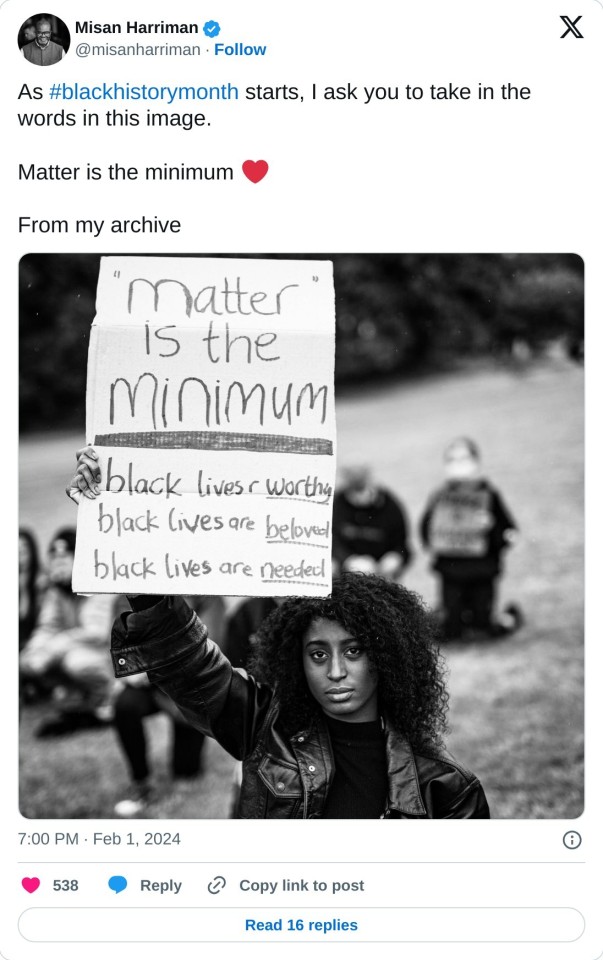
#black history is american history
Text
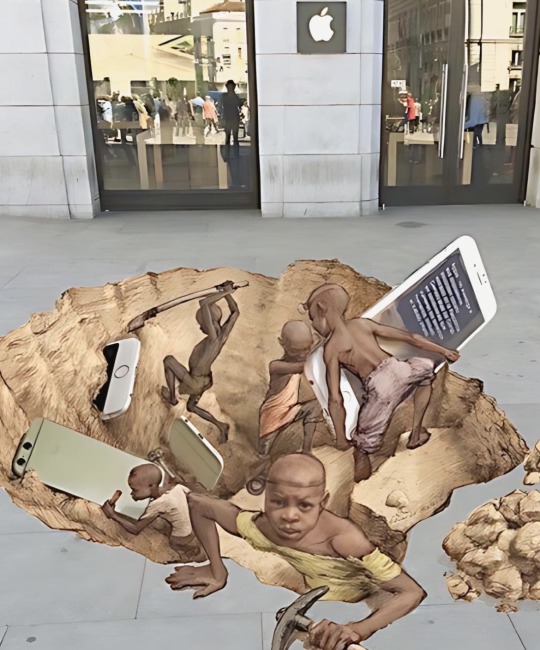

Congo is silently going through a silent genocide. Millions of people are being killed so that the western world can benefit from its natural resources.
More than 60% of the world's cobalt reserves are found in Congo, used in the production of smartphones.
Western countries are providing financial military aid to invade regions filled with reserves and in the process millions are getting killed and millions homeless.
Multinational mining companies are enslaving people especially children to mine.
•••
La República Democrática del Congo vive un genocidio silencioso. Millones de personas están siendo asesinadas para que la parte occidental del mundo pueda beneficiarse de sus recursos naturales.
Más del 60% de las reservas mundiales de cobalto se encuentran en el Congo, y se utiliza en la producción de teléfonos inteligentes.
Los países occidentales están proporcionando asistencia financiera militar para invadir regiones llenas de reservas y en el proceso millones de personas mueren y millones se quedan sin hogar.
Las empresas mineras multinacionales están esclavizando a la gente, especialmente a los niños, para trabajar en las minas.
Street Art and Photo by Artist Eduardo Relero
(https://eduardorelero.com)
#blacklivesmatter#blacklivesalwaysmatter#english#spanish#blackhistory#history#share#blackhistorymonth#blackpeoplematter#black history matters#black history 2023#black history is everybody's history#historyfacts#black history is world history#black history is american history#african history#black history#black history month#modern slavery#knowyourhistory#congo genocide#dr congo#blackbloggers#like#blackhistoryyear#follow#cobalt#blackownedandoperated#culture#art
11K notes
·
View notes
Text

For the ppl in the back!!
#black tumblr#black history#black literature#black excellence#black community#civil rights#black history is american history#civil rights movement#equality#equal rights#black lives matter#black pride#black people#equal#african slavery#american slavery#african american history#american history
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
I know Black History Month is over, but I wanted to share this masterpiece with y'all.
Credits: itsnotme3706 on Tiktok
Stay black, beautiful, and powerful, my people ✊🏾🖤🩶
#black reader#black writers#black tumblr#self post#tumblelog#black girls#poc reader#poc writer#black representation#black excellence#black history#black history month#black history is american history#malcom x#paisholotus
138 notes
·
View notes
Text

Black History is More than a Month
Art by Daeze Doodlez
#black art#illustration#black history month#art gives me life#daeze doodlez#black history is american history#natural hair
126 notes
·
View notes
Text

#negro league baseball#black excellence#black archives#black community#willie mays#birmingham black barons#baseball#black history is american history#black history#black pride#black culture
335 notes
·
View notes
Text
#Black history#global black on black love#black liberation#malcom x#african history#black power#black history facts#black history matters#black history month#black history is american history#black history 365#black lives are important#black lives fucking matter#black lives movement#blm#black lives matter
77 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ann Lowe was not only one of the most talented designers in the fashion industry in the United States during the 20th Century, she was also and remains one of the most iconic couture fashion geniuses (her dresses/gowns are just GORGEOUS folks -please check out the links I provided below to see some of her work!).
Ann Lowe was also the first Black person in America to attend and graduate from the S.T Taylor School of Design in New York City -she studied in classrooms by herself due to racial segregation, and despite the racist systems isolating her continuously she went on to open three shops of her own in the same city she studied in, and designed some of the most photographed and talked about dresses in the world -namely, Jacqueline Kennedy's wedding dress.
You can start to read a little more about her story here:
This incredibly talented, beautiful, and intelligent Black woman was an iconic couture fashion designer, but a lot of her work was not well-known in the fashion industry until recently, because she was rarely acknowledged for her designs -the wealthy/affluent people who bought her pieces did not want people to know a Black woman was making them. Although Ann herself prioritized her craft and later retired from the industry in 1972, I wanted to talk about her today because I just found out about her (frustratingly so -I wish I knew about her sooner). And that her legacy will continue to remain for generations to come.
"She transformed the fashion landscape, and her designs will inspire generations to come."
#feminist#feminism#black history#black history month#black history matters#black history is american history#united states#fashion industry#couture#fashion icon#ann lowe#america#museum of art#art#artist#dresses#dress#gowns#fashion#education#history#womens history#black women's history
87 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Unofficial Black History Book
Huey P. Newton (1942-1989)
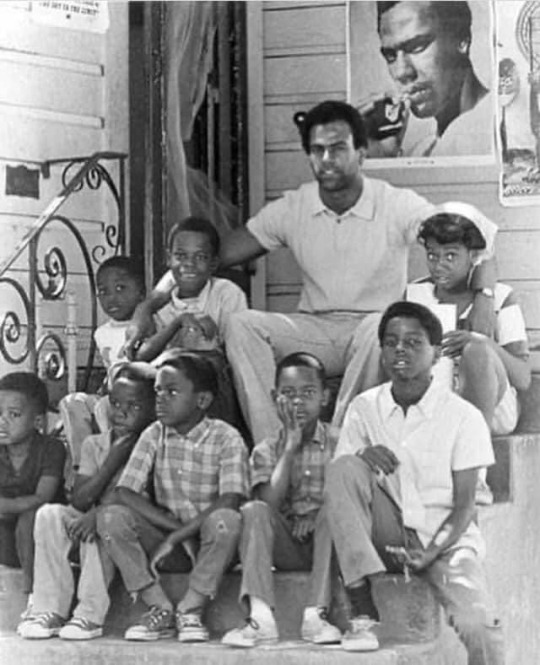
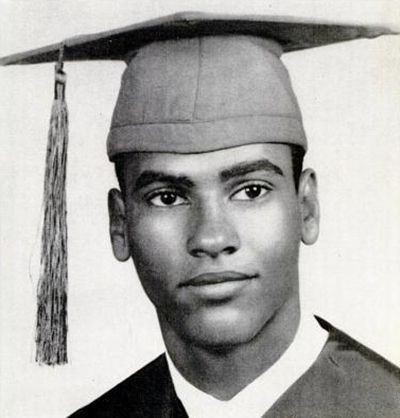
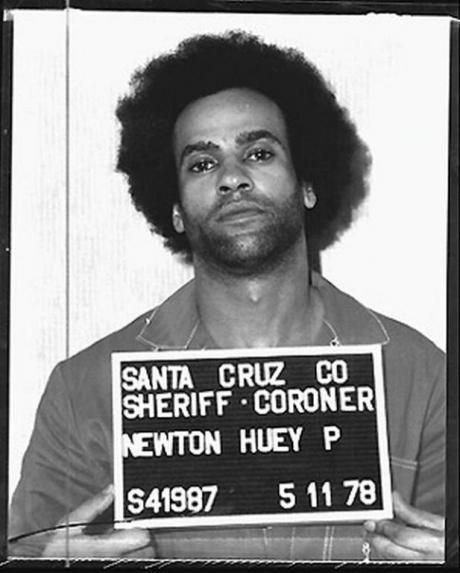
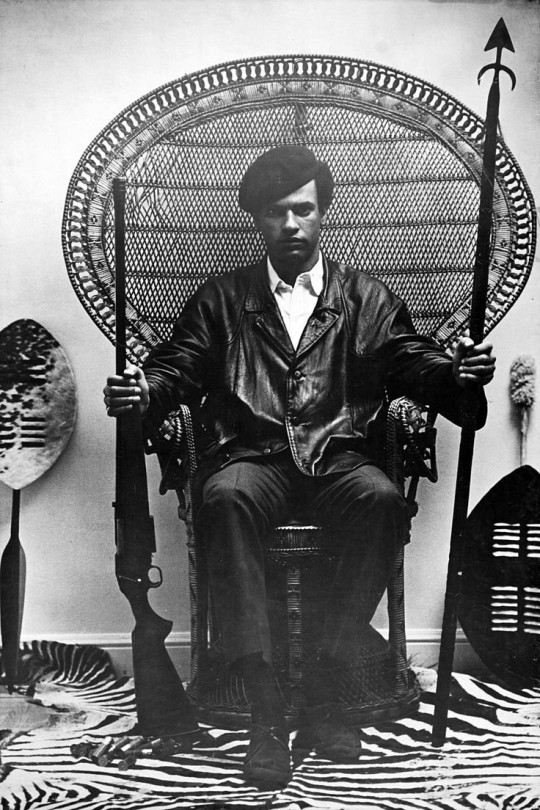








'The Revolution has always been in the hands of the young. The young always inherit the revolution.' - Huey Newton
This is his story.
Huey Percy Newton was born on February 17th, 1942, in Monroe, Louisiana. The youngest of seven children to Armelia Johnson and Walter Newton, he was named after former Governor of Louisiana, Huey Long.
His family relocated to Oakland, California, in search of better economic opportunities in 1945. His family struggled financially and frequently relocated, but he never went hungry or homeless.
Growing up in Oakland, Newton recalled his white teachers making him feel ashamed for being African-American, despite never being taught anything useful. In his Autobiography, ‘Revolutionary Suicide’, he wrote – “Was made to feel ashamed of being black. During those long years in Oakland Public Schools, I did not have one teacher who taught me anything relevant to my own life or experience. Not one instructor ever awoke in me a desire to learn more or to question or to explore the worlds of literature, science, and history. All they did was try to rob me of the sense of my own uniqueness and worth, and in the process nearly killed my urge to inquire.”
He also had a troubled childhood; he was arrested several times as a teenager for gun possession and vandalism.
Huey was illiterate when he graduated from high school, but he taught himself to read and write by studying poetry before enrolling at Merritt College.
During his time there, he supported himself by breaking into homes in Oakland and Berkeley Hills and committing other minor offenses. He also attended Oakland College and San Francisco Law School, ostensibly to improve his criminal skills.
He joined Pi Beta Sigma Fraternity while still a student at Merritt College and met Bobby Seale, a political activist and engineer. Huey also fought for curriculum diversification, the hiring of more black instructors, and involvement in local political activities in the Bay Area.
In addition, he was exposed to a rising tide of Black Nationalism and briefly joined the Afro-American Association, where he studied Frantz Fanon, Che Guevara, Mao Zedong, E. Franklin Frazier, James Baldwin, Karl Marx, and Vladimir Lenin.
Huey had adopted a Marxist/Leninist viewpoint in which he saw the black community as an internal colony ruled by outside forces such as white businessmen, City Hall, and the police. In October 1966, he and Bobby Seale founded The Black Panther Party for self-defense, believing that the black working class needed to seize control of the institutions that most affected their community.
It was a coin toss that resulted in Newton becoming defense minister and Seale becoming chairman of the Black Panther Party. Newton’s job as the Minister of Defense and main leader of the Black Panther Party was to write in the Ten-Point Program, the founding document of the Party, and he demanded that blacks need the “Power to determine the destiny of our Black Community”. It would allow blacks to gain “Land, bread, housing, education, clothing, justice, and peace.”
The Panthers took advantage of a California law allowing people to carry non-concealed weapons and established armed patrols that monitored police activity in the Black Community.
One of the main points of focus for the Black Panther Party was the right to self-defense. Newton believed and preached that sometimes violence, or even the threat of violence, is required to achieve one's goals.
Members of the Black Panther Party once stormed the California Legislature while fully armed in order to protest the outcome of a gun bill.
Newton also established the Free Breakfast for Children Program, martial arts training for teenagers, and educational programs for children from low-income families.
The Black Panthers believed that in the Black struggle for justice, violence or the potential for violence may be necessary.
The Black Panthers had chapters in several major cities and over 2,000 members. Members became involved in several shoot-outs after being harassed by police.
On October 28, 1967, the Panthers and the police exchanged gunfire in Oakland. Huey was injured in the crossfire, and while recovering in the hospital, he was charged with killing an Oakland police officer, John Frey.
He was convicted of voluntary manslaughter the following year.
Huey was regarded as a political prisoner, and the Panthers organized a 'Free Huey' campaign led by Panther Party Minister Eldridge Cleaver. And Charles R. Geary, a well-known attorney who was in charge of Newton’s legal defense.
Newton was found guilty of voluntary manslaughter in 1968 and sentenced to 2-15 years in prison. However, the California Appellate Court ordered a new trial in May 1970. The conviction was reversed on appeal, the case was dismissed by the California Supreme Court, and Huey was acquitted.
Huey renounced political violence after being released from prison. Over a six-year period, 24 Black Panther members were killed in gunfights with the police. Another member, George Jackson, was killed in August 1971 while serving time in San Quentin Prison.
The Black Panther Party, under the leadership of Newton, gained international support. This was most evident in 1970 when Newton was invited to visit China. Large crowds greeted him enthusiastically, holding copies of "Quotations from Chairman Mao Tse-tung," as well as signs supporting the Panther Party and criticizing US imperialism.
In the early 1970s, Newton's leadership of the Black Panther Party contributed to its demise. He oversaw a number of purges of Party members, the most famous of which was in 1971 when he expelled Eldridge Cleaver in what became known as the Newton-Cleaver split over the party's primary function.
Newton wanted the party to be solely focused on serving African-American communities, whereas Cleaver believed the party should be focused on developing relationships with international revolutionary movements. The schism resulted in violence between the factions and the deaths of several Black Panther members. The Black Guerrilla Family (BGF) was one of several factions that had broken away from the main party.
Then, in 1974, Newton was accused of assaulting a 17-year-old prostitute named Kathleen Smith, who later died, raising the charge to murder. Instead of facing trial, Huey fled to Cuba with his girlfriend at the time, where he remained for three years. The key witness in the trial was Crystal Gray. And three Black Panther members attempted to assassinate her before she gave her testimony.
Huey returned to the States in 1976 to stand trial but denied any involvement. The jury was deadlocked, and Newton was eventually acquitted after two mistrials.
In 1978, he enrolled in the History of Consciousness program at the University of California, Santa Cruz, and earned his Doctorate in 1980.
"War Against the Panthers: A Study of Repression in America," his dissertation, was later turned into a book.
On charges of embezzling Panther Party funds, Huey P. Newton was sentenced to 6 months in prison followed by 18 months on probation in 1982.
On August 22, 1989, Newton was assassinated by a member of the BGF, named Tyrone Robinson.
Huey was 46 years old at the time of his assassination. Robinson was convicted of Huey’s murder in 1991 and sentenced to 32 years to life in prison.
His wife, Fredricka Newton, carried on his legacy. 'Revolutionary Suicide,' his autobiography, was first published in 1973 and then republished in 1995.
Huey Newton was not perfect, but he did fight to protect the rights of the Black Community. The rights that we're still fighting for today.
__
Previous
Ruby Bridges
Next
Henry "Box" Brown
___
My Sources
#huey p newton#black community#the unofficial black history book#black activism#black history#black female writers#black history matters#black history is american history#black stories#black tumblr#black culture#history#writers on tumblr#writerscommunity#black power#black consciousness#black liberation#learn your roots#learn your history#black leaders#writeblr#black writblr#black writers of tumblr#black history 365#know your history#black panther party
90 notes
·
View notes
Text

#Black pride#black community#i love being black#black memes#black folks#black history month#black history#malcom x#global black on black love#black liberation#black power#african history#black history facts#black history is american history#black history matters#black history 365#black representation#self post#tumblelog#poc writer#black excellence#black reader#Black panthers#civil rights movement#turtle island#native americans#black panther party#malcolm x#black culture#black love
32 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Horrors of Lynching: Photographs and Postcards
Note to readers: This post contains graphic and disturbing images.

During the late 19th and early 20th century, thousands of photographs and postcards of Black Americans killed by white mobs in racist terror lynchings were collected, traded and sent through the U.S. postal service.
The postcards and photographs, depicting gruesome images of the bodies of Black men, women and children who had been tied to trees, mutilated, tortured, shot and burned alive by white mobs, were often distributed as souvenirs and saved as mementos in family albums and stored away in attics for safekeeping.
The lynching photographs often captured the bodies of the murdered Black Americans and the hundreds of white people — including children — who gathered to witness the public spectacle of lynchings. According to historians, in more than half of these photos and postcards, white people were shown smiling and celebrating the spectacles.
WHITE PEOPLE MONETIZED THE MURDER OF BLACK PEOPLE
Lynching photographs and postcards were shrewdly distributed — often for profit — across communities by hand and through the U.S. mail. They were often sold for as little as a quarter, which would be worth about $3.46 today.
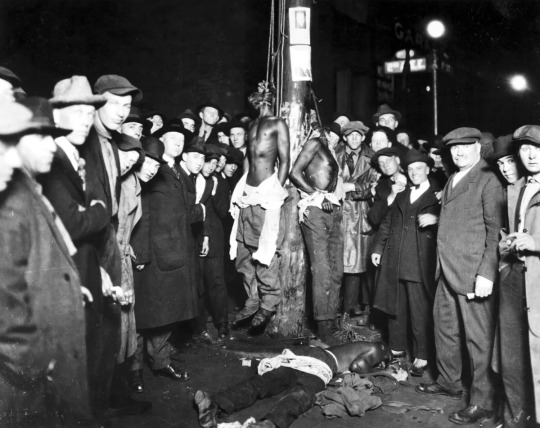

Source: wordinblack.com
Translated by Long Live Blackness by Shaneyra Thompson
•••
Los horrores de los linchamientos: fotografías y postales
Nota para los lectores: Esta publicación contiene imágenes gráficas e inquietantes.
Descripción de primera imagen: [Cinco afroamericanos fueron colgados de un cornejo en el condado de Sabine, Texas, en 1908 como "una advertencia para todos los negros".]
Traducción de la postal:
Esta es sólo la rama de un árbol de Cornejo;
Un emblema de la SUPREMACIA BLANCA.
Una lección que una vez se enseñó en la escuela de los Pioneros:
que esta es una tierra de GOBIERNO DEL HOMBRE BLANCO.
Una vez, temprano en la mañana, los blancos le dijeron al Hombre Rojo que enmendara su camino.
El negro, ahora, por gracia eterna, debe aprender a permanecer en el lugar del negro.
En el Soleado Sur, la Tierra de los Libres, que la SUPREMACÍA BLANCA sea para siempre.
Que esto sea una advertencia para todos los negros, o sufrirán el destino del árbol de Cornejo.
A finales del siglo XIX y principios del siglo XX, se recopilaron, comercializaron y enviaron a través del servicio postal de Estados Unidos miles de fotografías y postales de estadounidenses negros asesinados por turbas blancas en linchamientos terroristas racistas.
Las postales y fotografías, que mostraban imágenes espantosas de los cuerpos de hombres, mujeres y niños negros que habían sido atados a árboles, mutilados, torturados, fusilados y quemados vivos por turbas blancas, a menudo se distribuían como souvenirs y se guardaban como recuerdos en álbumes familiares.
Las fotografías de los linchamientos a menudo capturaban los cuerpos de los estadounidenses negros asesinados y los cientos de personas blancas (incluyendo niños) que se reunían para presenciar el espectáculo público de los linchamientos. Según los historiadores, en más de la mitad de estas fotografías y postales, se mostraba a personas blancas sonriendo y celebrando los espectáculos.
LOS BLANCOS MONETIZARON EL ASESINATO DE LOS NEGROS
Se distribuyeron astutamente fotografías y postales de linchamientos (a menudo con fines de lucro) entre las comunidades, en mano y por correo postal. A menudo se vendían por tan solo veinticinco centavos, lo que hoy valdría unos 3.46 dólares.
Descripción de segunda imagen: [Una postal de un linchamiento en Duluth. 15 de Junio, 1920.]
Fuente: wordinblack.com
Traducido por Long Live Blackness by Shaneyra Thompson
#blacklivesmatter#blacklivesalwaysmatter#english#spanish#blackhistory#history#lynching#black history is american history#historyfacts#black history is world history#black history matters#black history is everybody's history#black history 2023#black history#black history month#african history#blackhistorymonth#blackpeoplematter#knowyourhistory#blackhistoryyear#blackownedandoperated#historia#slavery#esclavitud#español#black tumblr#share#read#follow#blackbloggers
339 notes
·
View notes
Text
#tulsa oklahoma#black tumblr#race riots#tulsa#black history#black literature#black community#civil rights#black history is american history#american history#black wallstreet#black history matters#black history month
533 notes
·
View notes
Text
WE ARE BLACK! WE ARE BLACK HISTORY! ✊🏾










"Most people write me off when they see me.
They do not know my story.
They say I am just an African.
They judge me before they get to know me.
What they do not know is
The pride I have in the blood that runs through my veins;
The pride I have in my rich culture and the history of my people;
The pride I have in my strong family ties and the deep connection to my community;
The pride I have in the African music, African art, and African dance;
The pride I have in my name and the meaning behind it.
Just as my name has meaning, I too will live my life with meaning.
So you think I am nothing?
Don’t worry about what I am now,
For what I will be, I am gradually becoming.
I will raise my head high wherever I go
Because of my African pride,
And nobody will take that away from me."
We are BLACK Love
#happy black history month#black reader#black writers#black representation#black tumblr#self post#tumblelog#black girls#black excellence#black history is american history
716 notes
·
View notes
Text
Source: Aranivah | Links
#cumbia#black history month#afro latino representation#afro latino#colombian music#cumbia colombiana#black lives matter#black history is american history#indigenous people#indigenous lives matter#indigenous roots#afro latino history#mexican culture#mexican music#mexican american#black brown unity#bipoc representation#bipoc lives matter#bipoc
226 notes
·
View notes
Text

Gale Eugene Sayers (May 30, 1943 – September 23, 2020) was an American professional football player who was both a halfback and return specialist in the National Football League (NFL). In a relatively brief but highly productive NFL career, Sayers spent seven seasons with the Chicago Bears from 1965 to 1971, though multiple injuries effectively limited him to five seasons of play. He was known for his elusiveness and agility and was regarded by his peers as one of the most difficult players to tackle
#gale sayers#black tumblr#black history#black excellence#black literature#black community#kansas university#chicago bears#nfl#football#black players#nfl football#college football#black history is american history#blackexcellence365
230 notes
·
View notes
Text
Celebrating Black Queer Icons:
Miss Major Griffin-Gracy
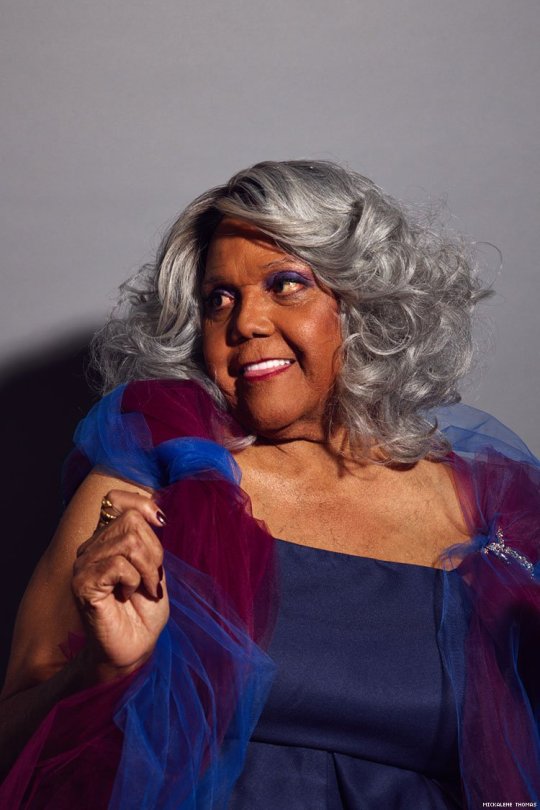

Born on October 25, 1940, Major is a trans women well known as a leader in the broader trans community and an activist, with a particular focus on black and incarcerated trans women. Major grew up in Chicago's South Side and participated in the local drag scene, during her youth. Major described the experiences as glamorous, like going to the Oscars. While she did not have the contemporary language for it, Major has been out as a trans women since the late 1950s. This made her a target of criticism, mistreatment, and violence, even among her queer peers. Majors transition, especially getting her hands on hormones, was largely a black market affair. Given the lack of employment opportunities for black trans women at the time, she largely survived through sex work and other criminalized activities. At some point Major moved to New York City and established herself amongst the cities queer community, despite the prejudice against trans women. She participated in the 1969 Stonewall Uprising. Later, after getting convicted on a burglary charge, Major was imprisoned with men at Clinton Correctional Facility in Dannemora, NY. There she met Frank "Big Black" Smith, a participant in the 1971 Attica Uprising at Attica Correctional Facility. He treated Major, and her identity as a woman, with respect and the two built a friendship. Smith also taught Major a good bit about advocating for herself and other trans women being mistreated by the US Justice System. Major was released from Dannemora in 1974. Major moved to San Diego in 1978 and almost immediately began working on community efforts and participating in grassroots movements. Starting by working at a food bank, she would go on to provide services directly to incarcerated, addicted, and homeless trans women, and would provide additional services after the AIDS epidemic started. In the 1990s Major moved to the San Fransisco Bay Area, where she continued her work, alongside organizations like the Tenderloin AIDS Resource Center. In 2003 Major became the Director of the Transgender Gender Variant Intersex Justice Project, shortly after its founding by attorney and community organizer Alexander L Lee, a trans man. The group works to end human rights abuses in the California Prison System, with a focus on trans, intersex, and gender variant POC. The position has since been passed on to Janetta Johnson, a previously incarcerated trans woman who mentored under Major. She is the focus of the 2015, award winning, documentary Major!. Major has five sons, two biological and three runaways she adopted, after meeting them in a California park. Her oldest son, Christopher was born in 1978, and her youngest, Asiah (rhymes with messiah) in 2021. At 82 years old Miss Major Griffin-Gracy continues to be an active member of her community and an advocate for our rights as trans people.
Haven't settled on which yet, but Willmer "Little Ax" Broadnax or Victor J Mukasa will be next!
#celebrating black queer icons#black history#black history month#black history is queer history#black history is american history#abolish the police#abolish prisons#decriminalize sex work#miss major griffin-gracy#major!#really disappointing to find out she doesnt show up in Popular Tags#stonewall inn#stonewall riots#stonewall uprising#transgender gender variant intersex justice project
335 notes
·
View notes
Text




Mouth Full of Golds. Written by director Lyle Lindgren and Eddie Pain.
A book of caps, fronts, slugs, and grills— even diamonds and pearls.” - lowereastcoast on ig.
#uploads#grills#slugs#mouth pieces#vashtie#photography#culture#black culture#black history is american history#black history month#Lyle#Eddie pain#lyle lingren#lyle lindgren
119 notes
·
View notes