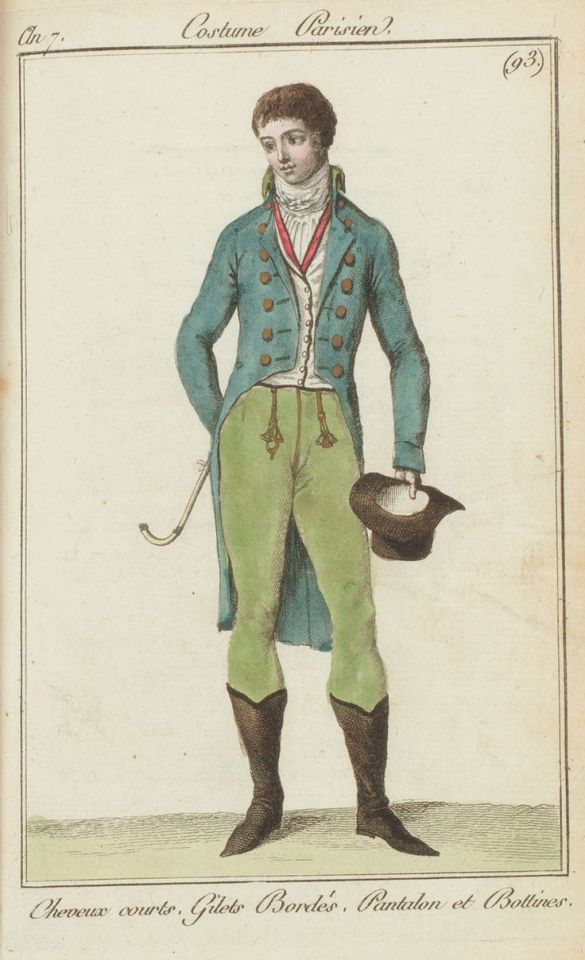
#Regency Men
Text




Fic Ship Meme:
Edwina Sharma and Dr Lucas Blakely, Earl of Greymoor in Only You Always by @tiffanytlee
#fic meme#ao3 fic#fic rec#only you always#edwina sharma#edwina sharma x oc#bridgerton#romance tropes#regency era#regency men#my edits#minimmakes
37 notes
·
View notes
Text


It's for a gay regency romance that I'm writing at the moment.
It's about a lord and his butler. The butler can see ghosts. That's why I wanted to include them in the cover. I've just finished outlining.
#gay pride#gay men#regency#gay regency men#regency au#grumpy x sunshine#butler x lord#master x servant#writeblr#writers on tumblr#self promo#book#regency men#bridgerton#bridgerton au
3 notes
·
View notes
Note
link & zelda regency era fashion please i’m on my hands and knees begging
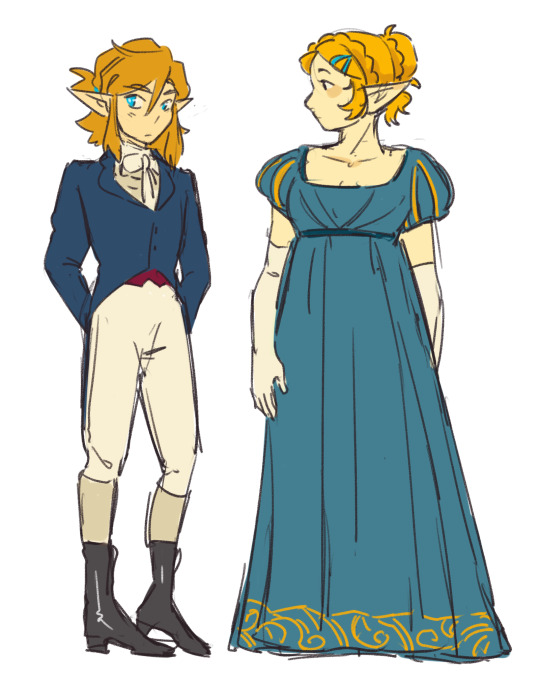

this might be the best ask ive ever recieved
#note that i did zero research beyond googling 'regency fashion' so if ur a historical fashion buff leave me alone#skribbles#asks#loz#almost also put link in a dress but i decided he can have a little suit moment for once. mens fashion in this era kind of slayed too tbh
910 notes
·
View notes
Text
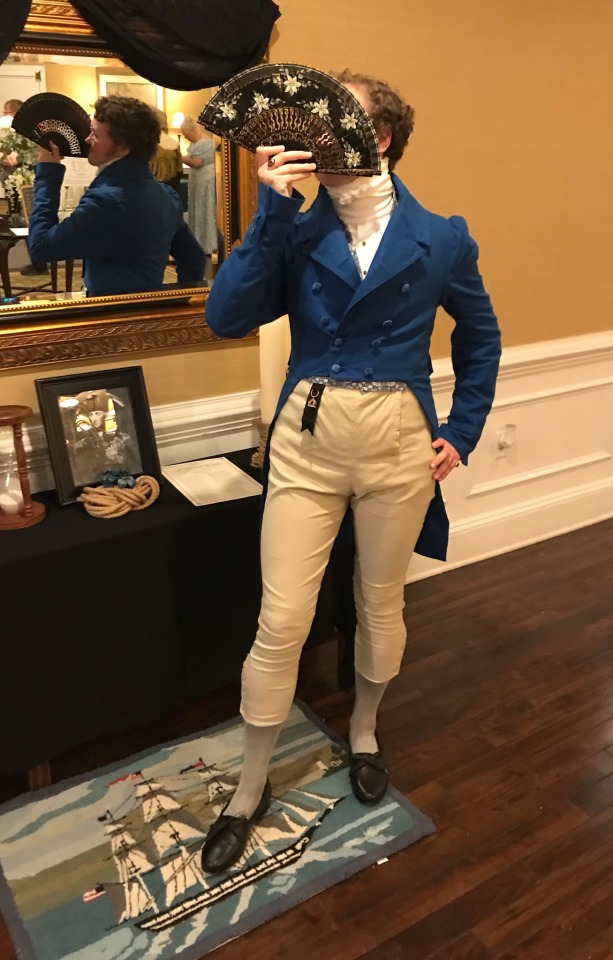
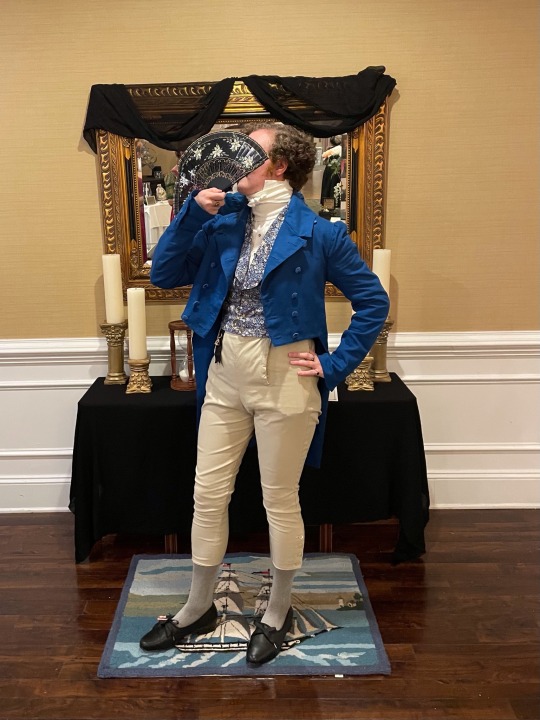
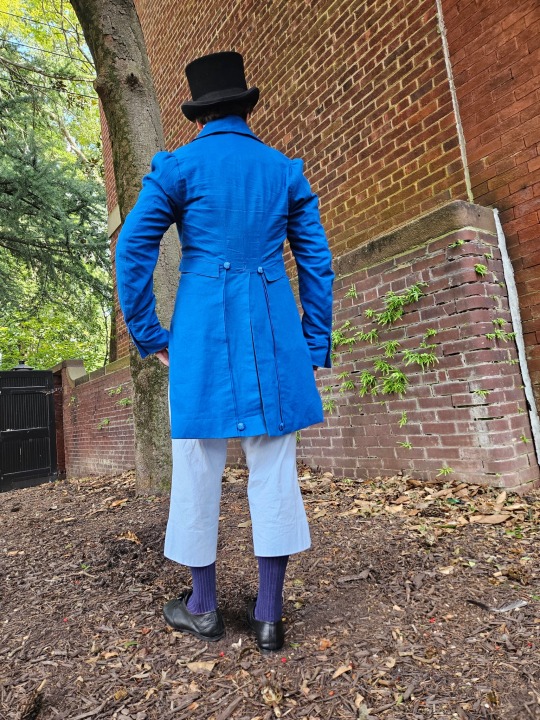




I spent quite a long time on this tailcoat and have gotten very busy without time to work on other projects, so I will dedicate a post to it.
Firstly big thank you to @vinceaddams for his deaths head button video which I used to make mine as well as links for making buckram!
Deaths head buttons weren’t really as popular any more by the regency period, but they still had Thread wrapped buttons for coats as well as one vest example I found for.
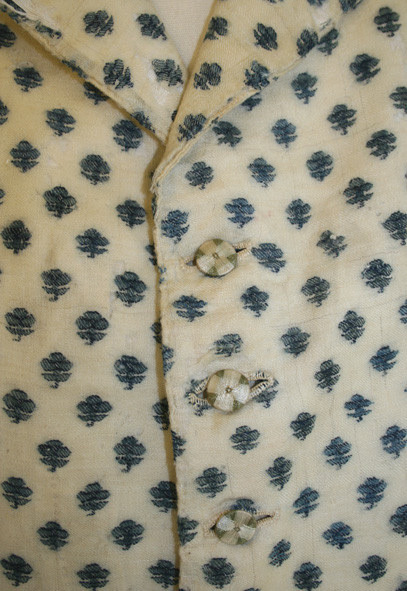
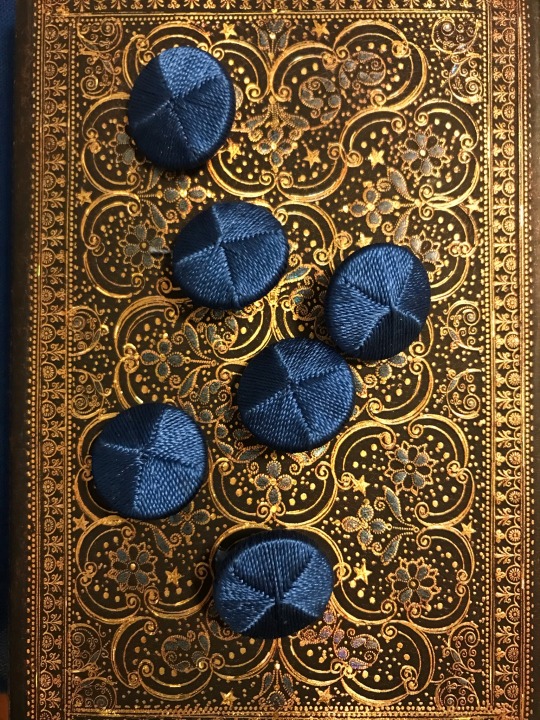



I made the buckram from scratch using linen I got at a second hand store and glue.
Decorative interior stitching was based directly off an 1830s tailcoat at the MET.



I used silk thread for all of the visible stitches, and it was like butter to hand-sew with. 100m/110 yds was more than enough for that as well.
(You can see the mutton chops I did :] )

#historical fashion#regency#1820s’ men’s fashion#menswear#regency men’s fashion#sewing#my post#fashion#regency fashion
433 notes
·
View notes
Text
one of the small things i love in the aubrey maturin series is how he constantly describes them as coming home from a social event or something and immediately undoing their breeches at the knee so they can be more comfortable when they're just hanging around the cabin or their house or whatever. i love details like that bc I'd never have thought of them but like. Of Course they'd do that
#same vibes as getting home & immediately unclipping your bra lol. but for regency men#thoughts#aubreyad#anyways submersive historical detail i love you
177 notes
·
View notes
Text

LayClaire Week Day 4: AU
“How ardently I admire and love you…”
I’m a big fan of Jane Austen and the Regency Era, so I jumped at the chance to combine it with my favorite franchise! (it looks so natural on Layton, hehe)
#this era is like the height of men’s fashion change my mind#layclaireweek24#layclaire#professor layton#hershel layton#claire foley#claire#fan art#flowertab#au#regency
101 notes
·
View notes
Text
I keep seeing people suggest Crowley's presentation in 1827 was feminine, and listen—headcanon what you want, I'm not your mom. But the justification is that he's supposedly dressed in feminine, as opposed to masculine, clothing? He isn't. You're just looking at Regency fashion with 21st-century eyes.


Both Aziraphale and Crowley are exemplaries of well-dressed gentlemen of the early 19th century, just in different styles.


On the left, a many-caped greatcoat like the one Aziraphale is wearing; on the right, a coat with puffed sleeves and a narrow waist like the one Crowley is wearing. (Both images seem to originate from Journal des Dames et des Modes, 1811 and 1826, respectively.)
I also saw something about Crowley's fob watch actually being a chatelaine?

Again, I have to disagree. What Crowley's wearing just looks like a watch chain, which both men and women wore. What you can see is the chain and a charm at the end; the watch itself is tucked into a pocket (same as with Aziraphale's).
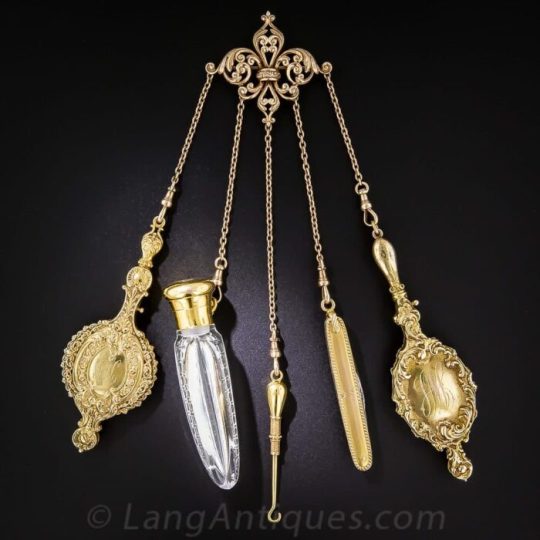


Watch chain (left; another plate from Journal des Dames et des Modes) vs. chatelaine (right, from here).
While a chatelaine could possibly refer to a decorative watch chain, the chatelaines specifically associated with women are the accessories worn by female heads of household or housekeepers (hence the name) to hold keys and other useful items. They could get quite elaborate. Crowley's doesn't look particularly like a chatelaine more than it looks like a watch chain, to me.
To sum up, there's not really anything I can see about Crowley's fashion choices in 1827 that specifically says "female presenting"; it all fits in with men's fashion of the time. You can headcanon whatever you want! But this particular era isn't one in which Crowley's wardrobe and styling definitively reads as feminine.
Note for a couple people with poor reading comprehension: TERFs are not welcome on this post. Fuck off.
#fynn posts#good omens#regency fashion#I am always Wary of wading into this especially because I've seen how spicy tw*tter-based fandom gets about interpretations#but it also irks me when people see men's fashion they don't understand and go “oh that's women's clothing”#so. yeah#1827? 1828? you know. around there. I missed that bit bc I was too busy failing to screenshot a gd watch chain#1828 was the westport murders but THAT'S ANOTHER POST
277 notes
·
View notes
Text
Why isn't the internet obsessed with Jane Rogan and Elizabeth Mothman they're gay they're time travelers they even had tried to kill each other before
#what more could you want#sons and sonsability is a masterpiece of podcasting and everyone should be obsessed with it#like time traveling regency lesbians who kill murderous men with servants named mario and wario whats not to love#dndads#dungeons and daddies#Jane Rogan#elizabeth mothman
232 notes
·
View notes
Note
https://www.tumblr.com/thebaconsandwichofregret/189924928150/comepraisetheinfanta-thebaconsandwichofregret
whenever i see people rbing the op without the additions i die a little inside so i thought you should have a go at debunking it 🫠
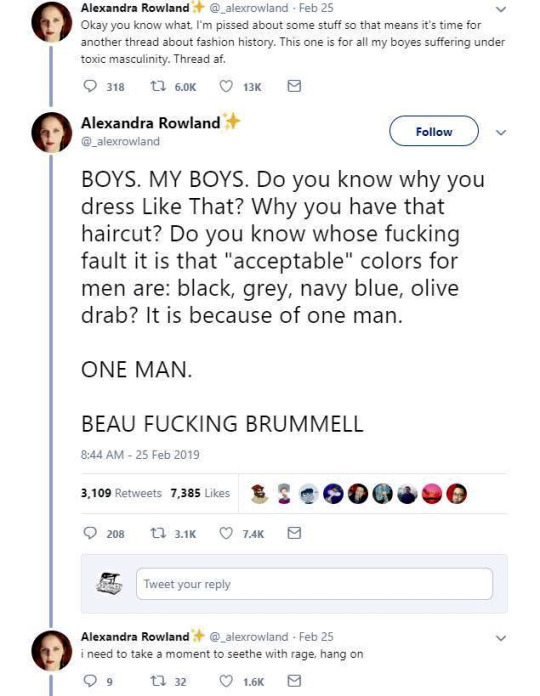


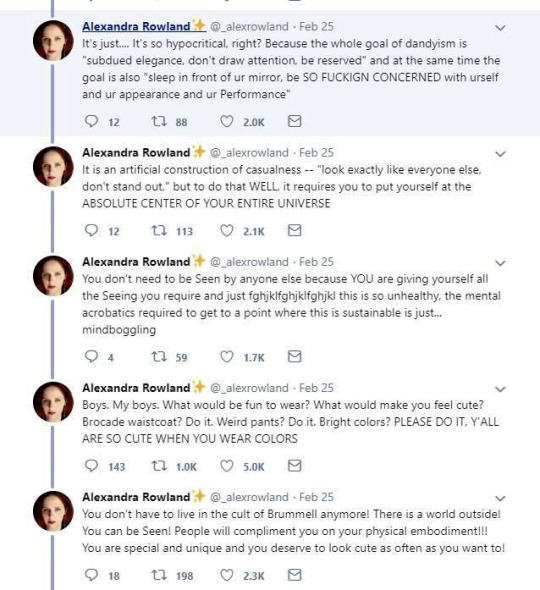
So these are the tweets from the post. I had blissfully not come across it before. This is one of the weirdest takes I have ever seen. It's amazing to see these fashion history takes that are so boldly and confidently wrong and inaccurate.
It's honestly hilariously ignorant to think that a massive cultural and societal shift that took couple of centuries, was all because one guy. It's so reductive and even goes to the great man territory to pick one person to blame for something like this that really had much more broad and complex reasons than "a guy did it". It's stressed in this tread that Beau Brummell was not noble or a gentile and "just some guy", so how would he singlehandedly change the fashions and concept of masculinity of the whole western world? He was a London socialite, it's not like most of his contemporaries in continential Europe knew about him. Like maybe the French, but does anyone really believe people in Eastern-Europe or Nordic countries or in the Mediterranean knew about? Not to mention places like US. Yet everyone dressed like that in his lifetime, so how could his influence reach so far so quickly? Not even kings and queens could so directly and massively shift the fashions. So in the face of it the whole claim is ridiculous, but it's also full of inaccuracies.
The shift from Rococo fashion to regency fashion was extremely stark and quick in both men and women's fashion, but it happened during 1780s and 1790s, before Beau Brummell became a well known figure in the London society (he was born in 1778 and became well-known in the society after his military career, during which he befriended the Prince of Wales, around the end of 1790s). Here's first an example from 1780s and then from 1793-94 and 1797.
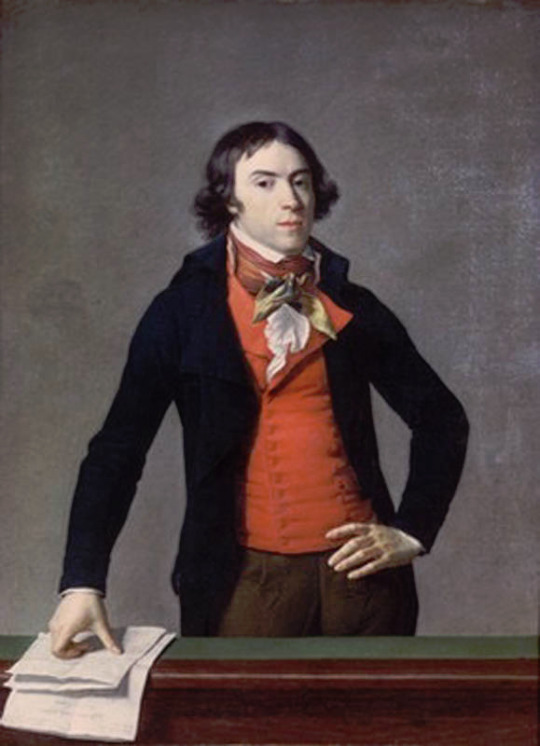



The one from 1780s still has some rococo elements like the wig, but it's already much more toned down and the coat is already turning from frock coat to a tail coat. It's an example of the more casual men's countryside dress from the period. The court dress was still quite elaborate, though also toned down from the 1770s. But there's a big shift when it comes to the examples from 1790s. They are unmistakably Regency fashion. All of these example are French too. I'm sure these people had no idea and gained no influence from an unknown middle class English officer. So what did actually happen? Well, I'm pretty sure the French Revolution in 1789 had a little bigger impact on the European society and fashion than Beau Brummell.
I'm not going to go too deep into this, since I'm working on an in depth post about the masculinity and fashion in the modern era and I go into detail about how the French Revolution had a massive part in shaping them. But the short version is that the French revolutionaries rejected the elaborate fashions of the Rococo French nobility (in both men and women's fashion) as those over the top fashions stood as symbols of the excess wealth of the nobility and the extreme wealth gap between then and the rest of the people. This is also why the high fashion was getting toned down thorough the 1780s before the Revolution. The anger towards the ruling class was mounting at the time and it encouraged the nobility to down down and try to act a little more palatable in their aesthetics to maybe appease the angry people without doing any actual change to address the wealth gap and the centralized power.
The revolutionaries looked for ideal masculinity and femininity elsewhere then. To contrast themselves against the ruling class, they looked to the antiquity and it's simplicity as well as the peasantry and the country gentleman fashion. Romanticism was the driving force behind the artistic expression of the Revolution. It weaved nationalism to the class struggle that was at the core of the revolutionary movement. So the Revolution was not just the working class and peasantry against the ruling class, but the French People against the nobility. This is when physical labour, militarism, dominance and leadership, really became intrinsically attached to masculinity, as the ideal man of the revolutionaries was a working peasant, who with military power took the the power back to the people from the nobility. The democracy would not last long, but it's not a mistake that only men could vote under the new democracy after the Revolution was won. It's also not a mistake that even when the post-Revolution France eventually abolished slavery (but not without some push-back first and a couple of slave revolts to force their hands) they did not give most people of color rights to vote. Since colonialism whiteness had become intrinsic part of masculinity and femininity, which was part of the dehumanization of everyone else, and the new form of masculinity and femininity born out of the Revolution did not contest that. In fact the Enlightenment philosophy that had laid the ground work for the Revolution and the Romantic movement and it's nationalism that were driving force in it, in no way contested colonialism or it's white supremacy. Which is why the power in the new democracy went to the (mostly) white men.
These elements were in the new men's fashion too. Nationalism, the idealization of militarism and antiquity seen as the origins of democracy made it and especially Antique Rome perfect inspiration for the Revolutionary France. The short hairstyle was inspired from the Roman fashion seen in statues. The fashionable tail coat was influenced by military uniforms and the short jackets of the working class. The long trousers also came from working class dress. Here's examples of the revolutionary fashion from first 1792 and then around 1790.
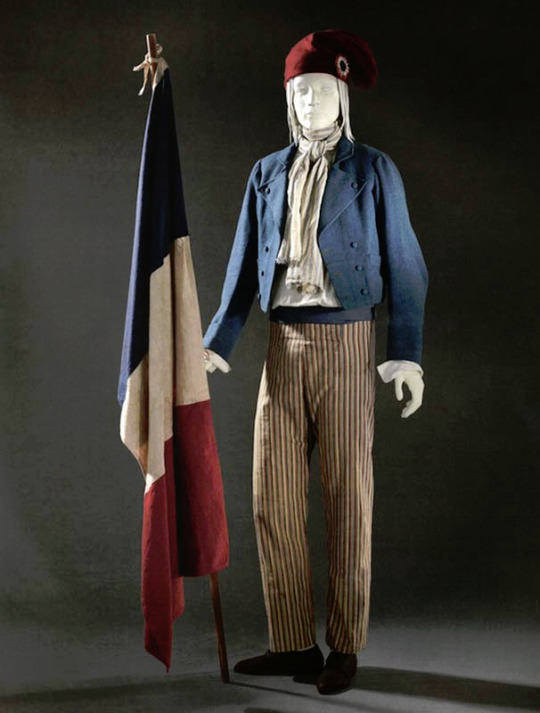


To be very clear, the revolutionaries were not a single entity with single ideology. They were collection of movements, who were united in their shared desire to overthrow the ruling class and establish some sort of democracy. But inside the movement were much more radical movements than what eventually ended in power after the French nobility. Socialists, abolitionists, feminists, slaves and others also fought for the Revolution and there was a lot of internal struggle too. Romantic movement was also very varied and contained extremely nationalistic elements as well as outright socialist elements.
Beyond the direct and stark effect the French Revolution had in especially France, but everywhere in the western world, the 18th century fashion was never as extreme as in France. If you put the most elaborate French court fashions of mid 1700s and Beau Brummell's style next to each other the difference is certainly massive, but fashion for men as well as women was always much more restrained and somber in England. Here's an English example from 1755-65 and for comparison a French example from 1755.
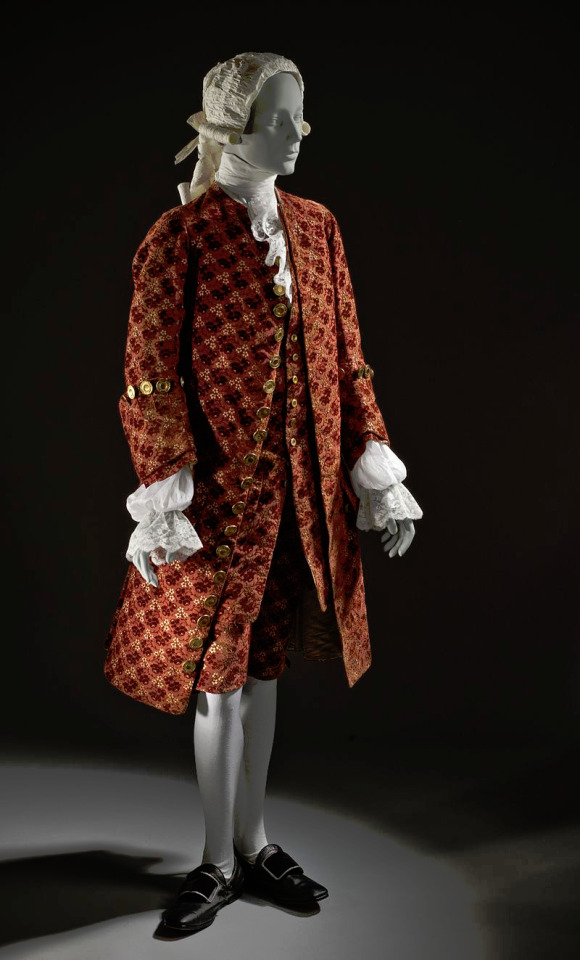


In fact as the tensions were rising in France the upper class begun to adopt the more toned down English styles. After the Revolution the new Republican styles would spread to Britain too. In Britain though Romanticism had a more pronounced effect as it stayed firmly monarchist. Therefore the English fashion was especially influenced by the styles worn by country side gentlemen.
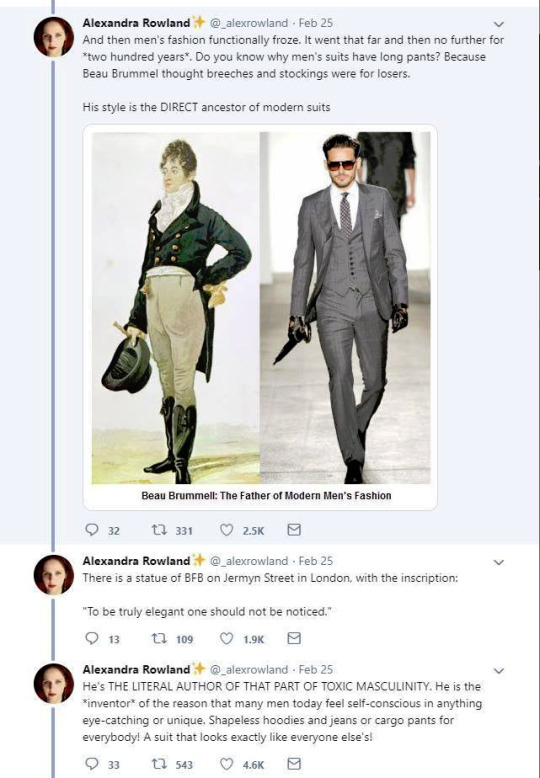
There's another claim in the thread that fully fails to understand the broad implications of fashion and societal gender and how these things change and evolve. It's the claim that Beau Brummell created the modern men's suit and he's the reason the suit has long trousers. We already went through how long trousers got into men's fashion and it was not him. But the writer is not wrong in saying that Beau Brummell's outfit in this picture is a direct ancestor of modern men's suit. It is.

But you know what else is a direct ancestor of men's suit? This.
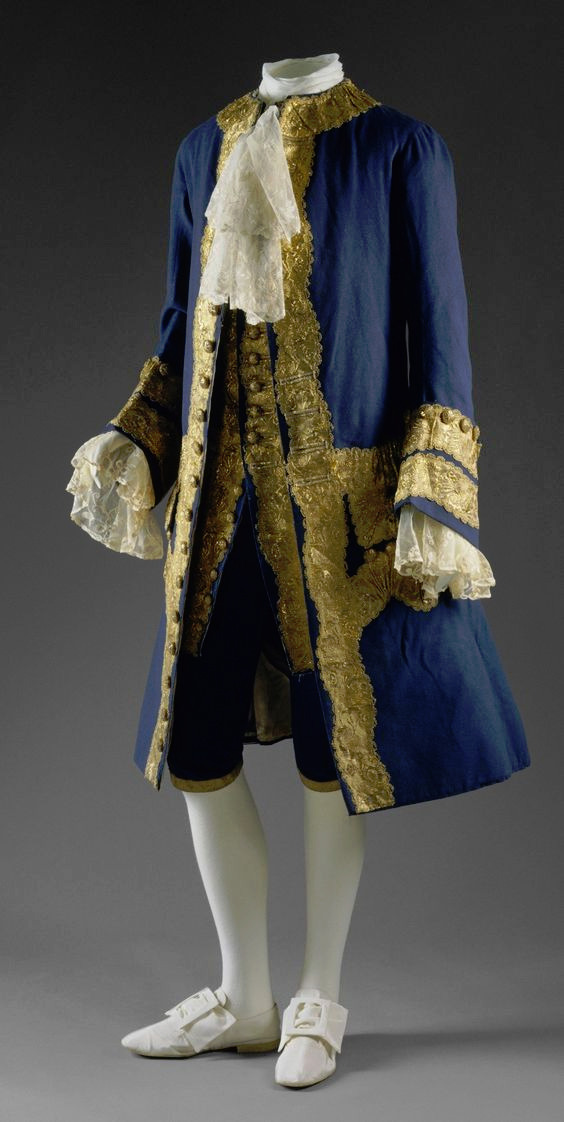

The modern three piece suit has it roots as far as in late 17th century. Before suit men wore doublets, which style resembled women's fashion much closer than the suits would after it (as seen in these examples from 1630s). However the distinction between men and women's fashion had started to grow much earlier. A big shift that happened during the 16th century was that men stopped wearing skirts. Men and women wore the same garments for centuries before that. The styles and silhouettes for men and women had some differences (the skirts were often shorter for men for example) but they were parallel to each other. I wrote a whole very long post about how skirts stopped being acceptable for men. In it I write about how the shift in men's fashion was part of the large shift from feudalism to colonialism and capitalism, that needed a new hierarchy to justify the new system after the previous divinely justified feudal hierarchy was no longer an option. The new hierarchy was white supremacist patriarchy and therefore needed a clearer distinction between white men and white woman, that would also help distinct white people from the racialised people.
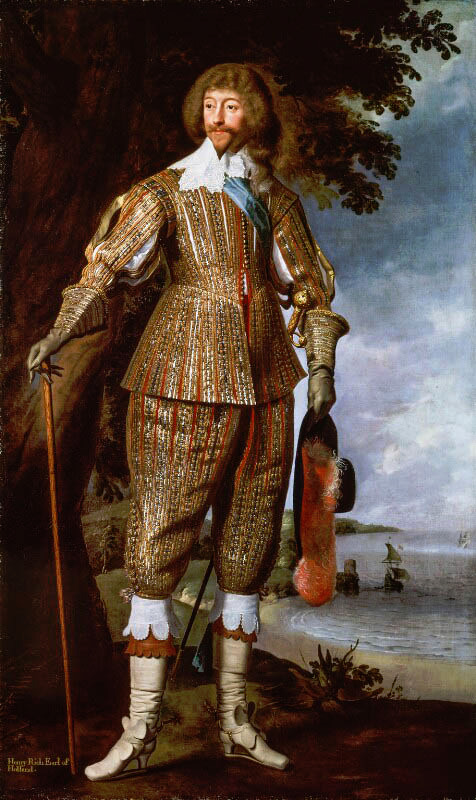


But such fundamental changes in the societal structure and culture are long processes. The process was continuing in the latter half of the 17th century, when Orientalism first became very popular. Orientalism is the dehumanization and fetishization of Asia and North-Africa, and it was born as the European colonial project was properly getting going in Asia. Colonialism in Asia and North-Africa took a little different form. I suspect it was because it was not that long ago, when Europeans had felt inferior to many of the peoples and empires in Asia and North-Africa, which they had always had much closer relationships with than the rest of Africa and certainly the Americas. I think that's why Orientalism is such a mix of coveting Asian and North-African cultures and bodies in a very fetishistic ways, while also demeaning and diminishing them. Nevertheless, Orientalism had a huge impact on European fashion in late 17th century. Both the way men and women's clothing was made after that to this day was strongly impacted by Orientalism. The coat and waistcoat combination was an adaptation of Turkish fashion. The three piece suit became popular in 1670s and fully took over men's fashion in 1680s (an example from 1687). The cravat was also adopted around the same time to men's wear from a light cavalry mercenary army in the Habsburgian Empire known as the Croats or Cravats. They were mainly Croatian, which to Western European was almost "Oriental" due to their proximity to Asia and Turkey in particular, and therefore the popularization of cravats as a fashion item was also influenced by Orientalism.
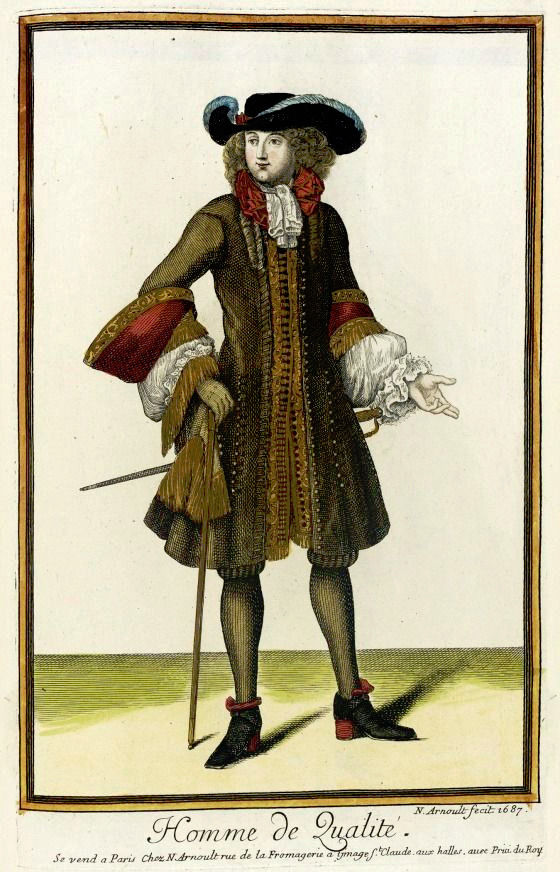

The Regency three piece suit also has all the same elements as the suit 150 years earlier, the individual pieces had just evolved into different different cuts. The three piece suit in fact still has the same elements to this day, they have just kept evolving.
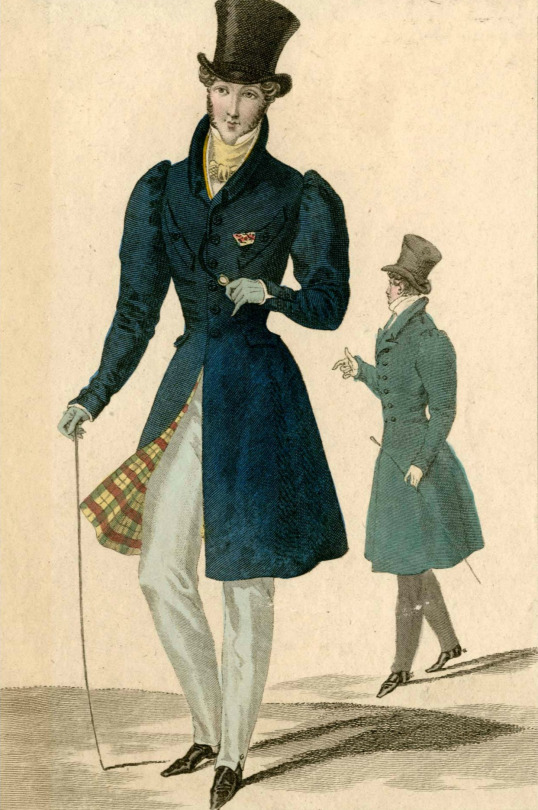
My point is not to in any way deny Beau Brummell's influence on Regency fashion. He was the most influential fashion icon for men in his era after all. I hope this just made it very clear that these bigger changes are not about individual people but much larger shifts and movements in society and culture. His actual influence was popularizing some of the English countryside styles mentioned before in the fashionable London society, making extremely elaborate cravats into the fashionable items of the day and becoming the image of the English dandy.
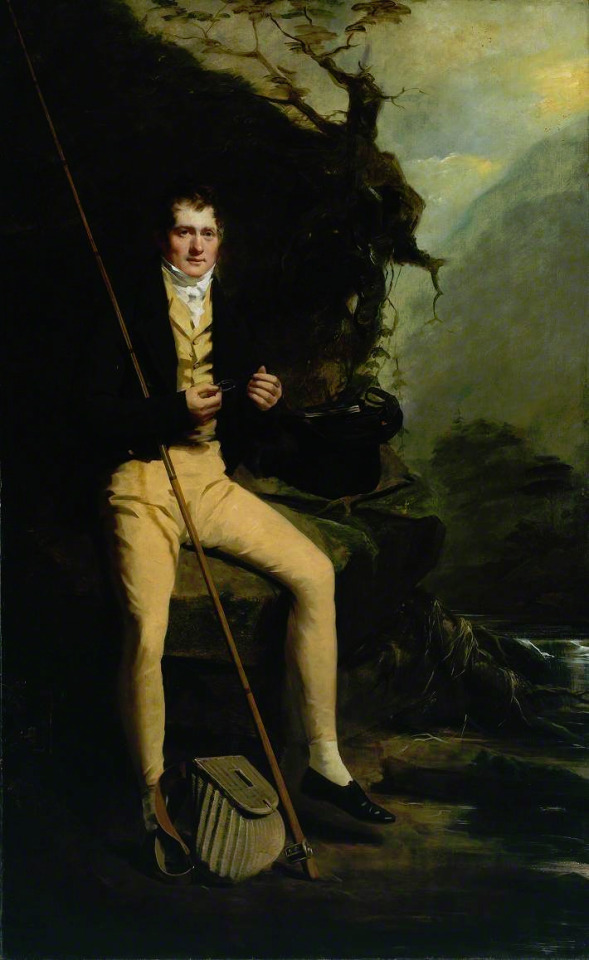
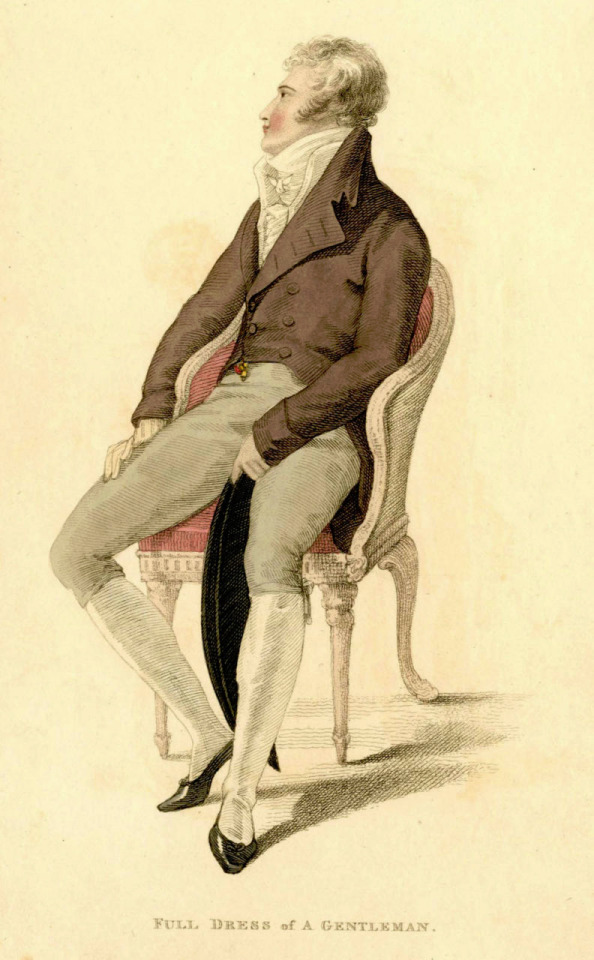
The picture of him above shows him the typical English countryside suit with dark blue tail coat, white cravat and light pantaloons with polished hessian boots. He helped to make the outfit and pantaloons in general fashionable. Breeches would stay as the formal leg wear for some a decade still, till young fashionable men would start to use black or gray pantaloons in formal events too. Pantaloons were very fitted, but the trousers, that were fashionably quite narrow at the time, but looser, really came into the casual fashion in 1810s. As seen before their roots come from the working class fashion that was first popularized in the French Revolution, but they had been very informal and while they were still not quite as formal to be able to use in a formal event, they became acceptable in more casual events. Beau Brummell is credited for inventing or at least popularizing pants that have strap to go under the foot in order to keep them straight. Here's first a painting from of a gentleman in a very country style emphasized by the setting. Then a illustration from 1810 of a full formal dress with breeches and a fashion plate from 1817 of day wear with trousers.



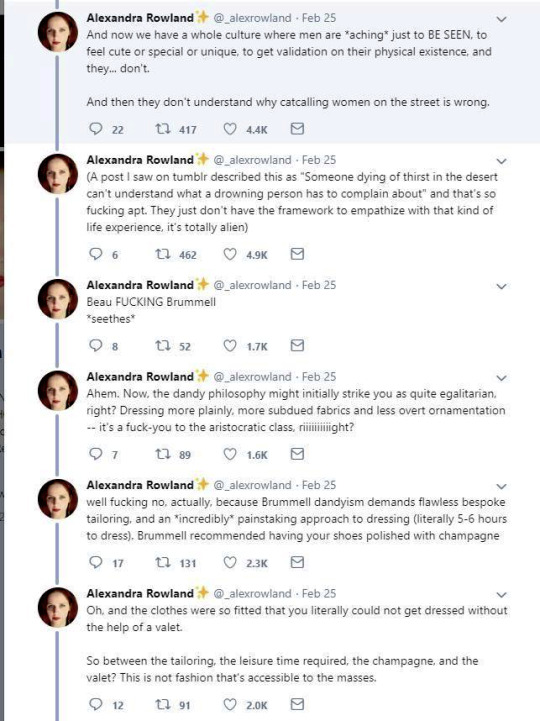
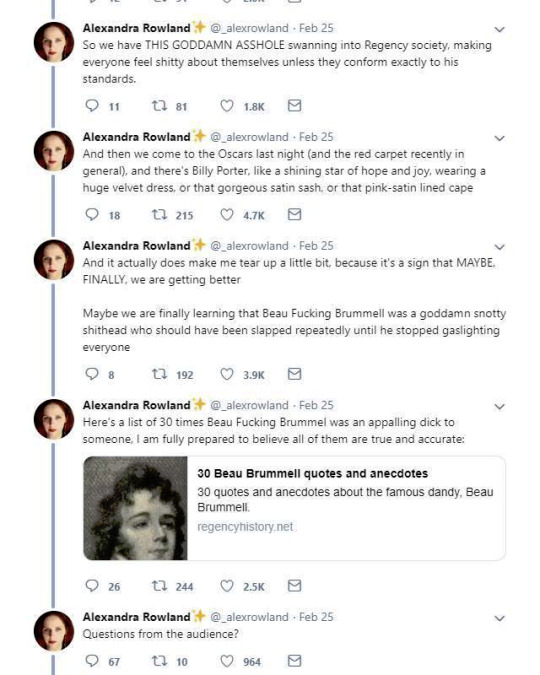
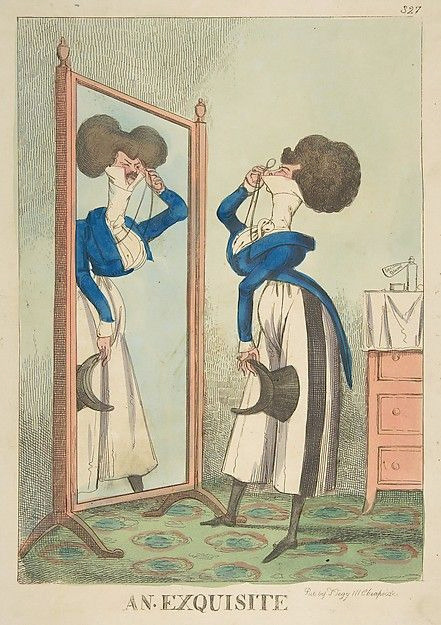
The thread also misses what dandy really was. Dandy was the embodiment of the middle class social mobility of the modern era. He was the "self-made man", the fashionable middle class and the new celebrity of a post-feudal era. He dressed in refined fashionable countryside middle class clothing and was celebrated for his style and refinement, not for his birth. Ironically though, there was a distinct reactionary quality to the Regency dandy. After all dandy did not embody social equality, but mobility. He was the ideal man of the capitalist hierarchy. A bit of dilemma for the dandy was that being extremely fashionable was central to the dandy, but after the French revolution being too fashionable and too concerned about looks had been associated with the aristocracy and was now therefore unmanly. Which is why dandy quickly came to be seen as effeminate. There is a lot of satiric cartoons from the time period that make fun of dandies and their preoccupation with fashion and looks. Here's couple from around 1810s.



In conclusion it's pretty ridiculous to say modern men's fashion was all created by one guy. The real reason why men's formal suit (and to be clear more colorful and elaborate styles have come and gone from men's informal fashion during that time) has been what it is for more than hundred years is because much bigger changes, like capitalism, colonialism, Orientalism and white supremacist patriarchy.
#fashion history#dress history#history#regency fashion#historical fashion#men's historical fashion#18th century fashion#answers#anon
362 notes
·
View notes
Text
s4 was actually so incredible in terms of development. Kitty becoming more self assured and confident. The way julian and alison got on (the guy who lost his daughter and the girl who lost her father) so much better compared to season 1. Robins love of life expanding from curiosity to outright looking over a rat family and redirecting lightning to save mike. thomas is there i suppose. The Captain being more open about his ideas and things he likes, things we never saw in season 1 or 2. Mary’s entire fantastic story that i thoughts about that i simply can’t put into words. Pat having to confront both sides of a loved one passing on, both being the loved one and having to comfort others. Fanny going from thinking Alison was a prostitute to defending her when Thomas wouldn’t stop his remarks, her internalised misogyny taking further of a back seat. the collective development from season 1 where they wanted alison to leave, to leaving a glowing 5 star review for their gatehouse. i love this show so much.
#i’m utterly convinced thomas is representative of men/incels who don’t change and can’t take no for an answer#and mat just wanted to dress up in regency attire#bbc ghosts#10:30 gn gang
246 notes
·
View notes
Text
I wish people would focus less energy on weird 19th century stuff that has been widely debunked, like the idea that Victorian women constantly fainted, and START focusing energy on weird 19th century stuff that definitely DID happen, such as the many decades that men carried around decorative canes for Fashion purposes. The silly little stick era, if you will—"He carried a little stick of no earthly use", Albert Smith, The Natural History of the Gent.
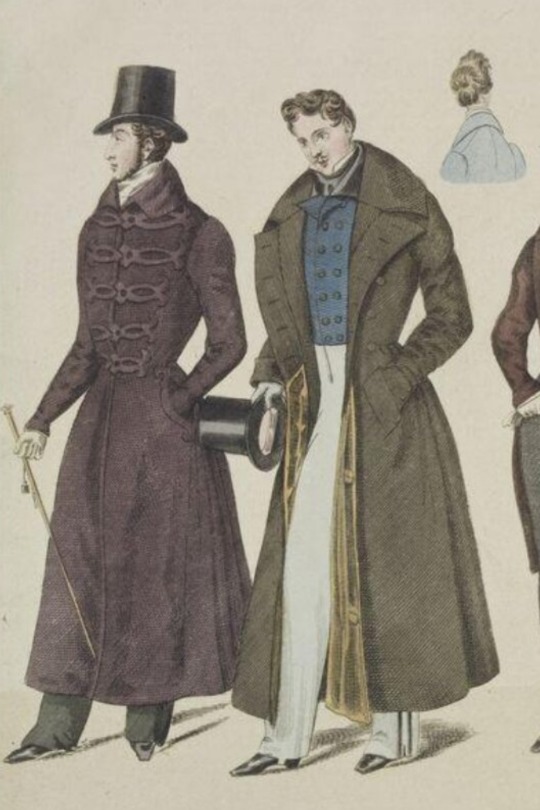

1832 fashion plate (with bonus hairdo), and you can see that the gentleman at left isn't even touching the ground with his stick, he's just carrying it. There are countless fashion plates like this, and even when the stick is the correct length, it often looks flimsy and isn't a true mobility aid.

Somehow, even the child has acquired a little stick in this 1867 fashion plate. The man next to him has his stick tucked under his arm, which seems to be a typical way of carrying it, or you could even tuck it into your coat pockets.

1840s dork has never heard of coat check, idk.
Two fashionable fellows in Punch magazine, 1842, just carrying their sticks.
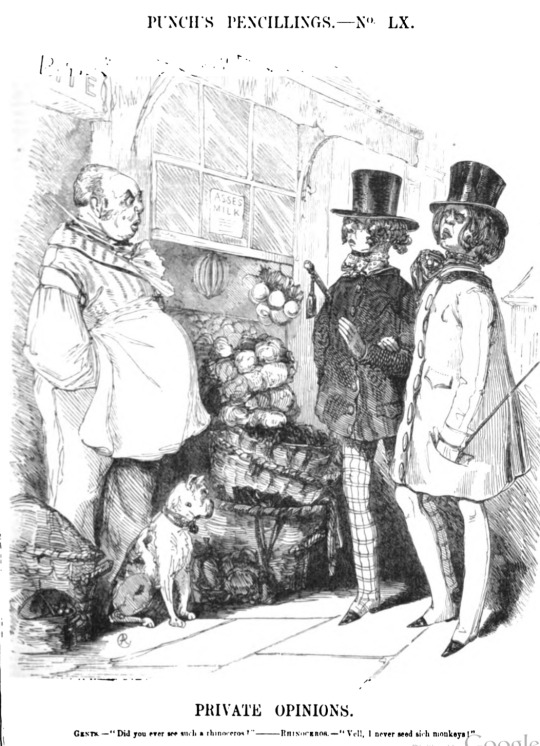

I'm throwing some pictures together on my lunch break so this has an 1830s/1840s slant, but you will see the little sticks from the dawn of the 19th century to the end: able-bodied men really chose to be encumbered with these for no good reason. Sometimes they're topped with tassels, or a quizzing-glass!
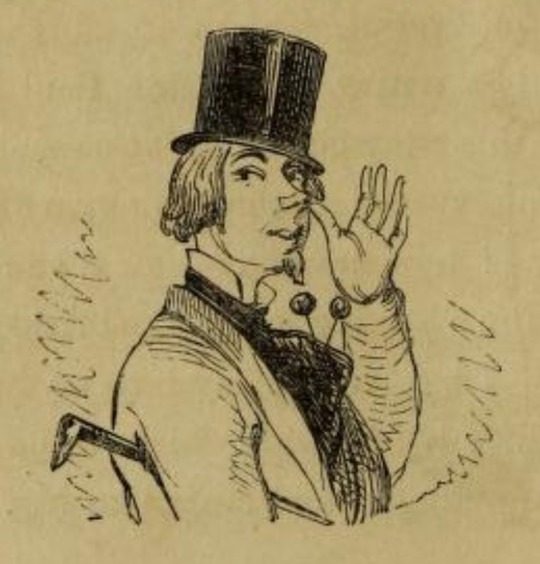

#fashion history#men's fashion#historical men's fashion#19th century#regency#victorian#accessories#canes#walking sticks#fashion#shaun talks#1840s#sorry this is so 1840s i live to make fun of 1840s men
2K notes
·
View notes
Note
How's the market for Regency fellows? There seems to be a trend towards early Victorian men, but I'm interested in finding a 19th century man who really suits my tastes & lifestyle. Would you recommend a Regency companion for a scholar-writer outdoors(wo)man?
Indeed, this blog has a bias for the plaid-clad set. But who can ignore the appeal of a Regency man!
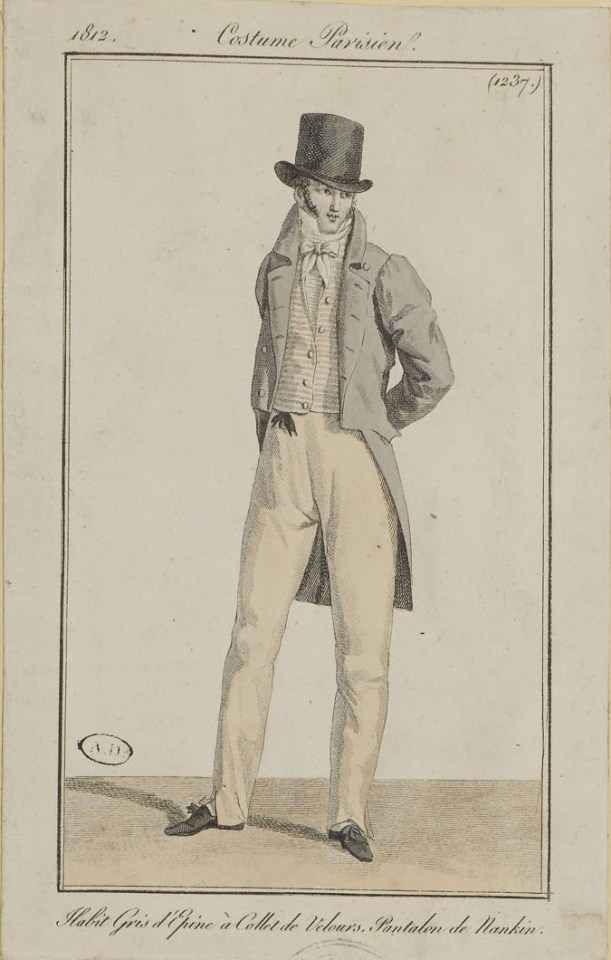

Many appreciate him for the ease of his "country gentleman" look, with equestrian boots and pantaloons, and clothing that shows his figure to great effect.
When you are looking for a Regency era man in his physical prime from an educated background who loves the great outdoors, out of necessity you are drawing from a pool of largely military men. If this isn't what you want, you may have a hard time avoiding the sashes and epaulettes and paintings of Washington, D.C. in flames.
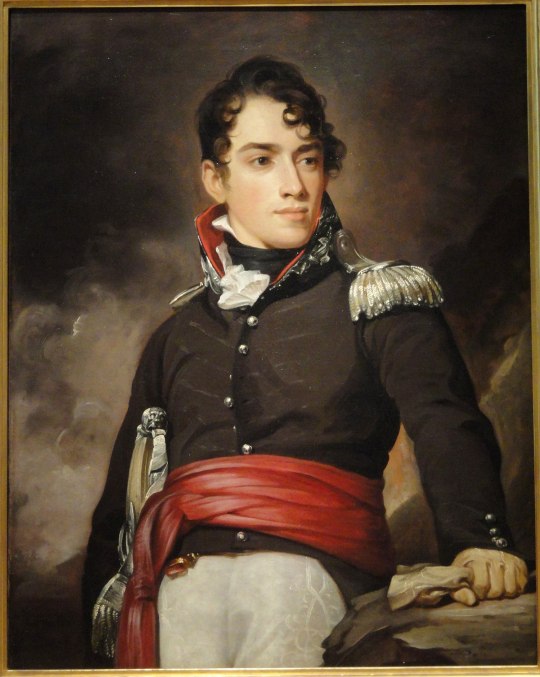
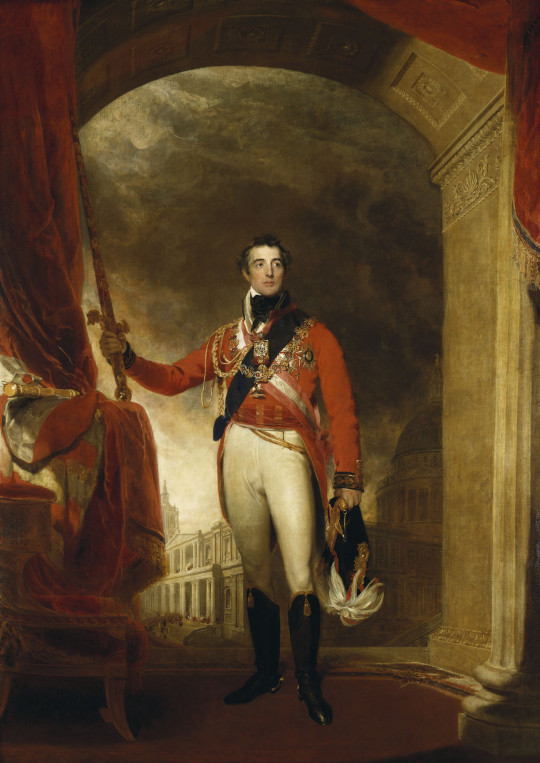
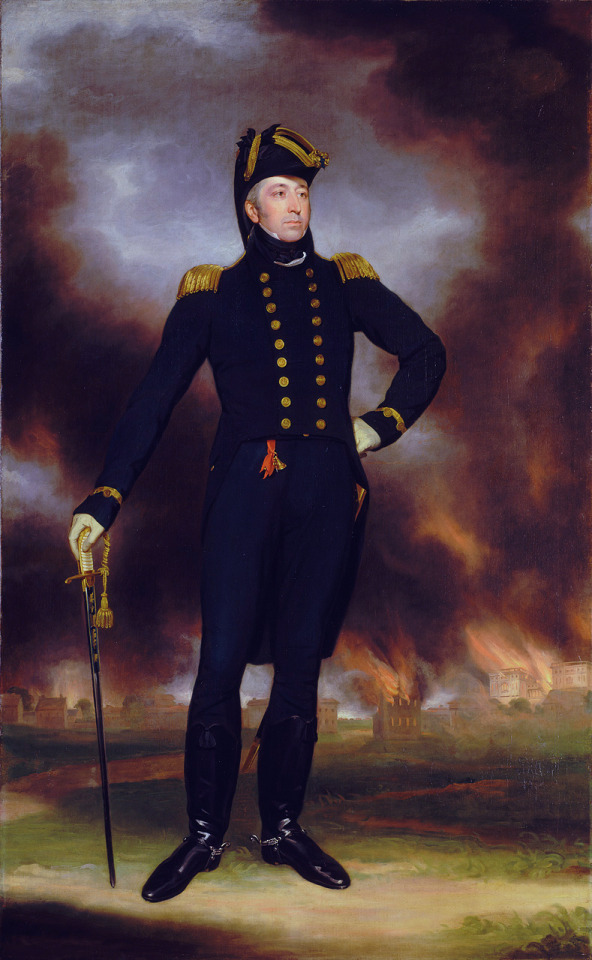



The man of the 1810s has a lot to offer, but his needs for conflict and conquest can be high! Be prepared for voluminous correspondence, long periods away on campaign, and an absolute requirement for a manservant to attend his wardrobe and toilette.
54 notes
·
View notes
Text
Jonah: The love interest.
Barnabas: The boot licker.
Albrecht: The Simp.
Mordechai: The Sugar Daddy.
Fanshawe: The Ex.
Simon: Not in love with Jonah he just likes to paint him.
Peter: Husband.
#Jonah 'Slut who goes through men quicker than I go through markers' Magnus#Simon Fairchild and Jonah Magnus have a father/son relationship in my mind#Any time I read a fanfic with the two that's just the vibe I get#I know nothing about Mordechai...but he's probably a dick#Jonah just wants his money#RIP Barnabas Bennet#jonah magnus#peter lucas#mordechai lukas#albrecht von closen#jonathan fanshawe#simon fairchild#tma regency era#tma#Jonah Magnus's harem#coming soon#the magnus archive#lonelyeyes#tma headcanons
148 notes
·
View notes
Text
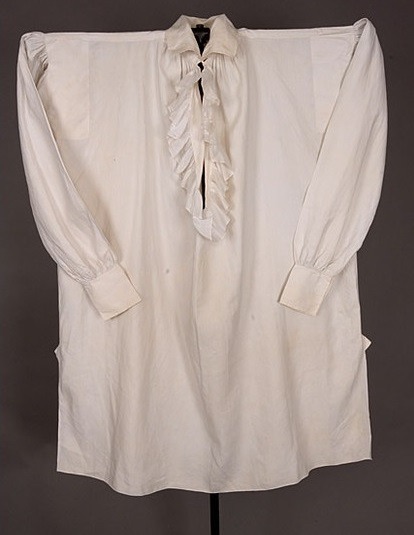

Man's linen shirt, 1800-25.
64 notes
·
View notes
Text
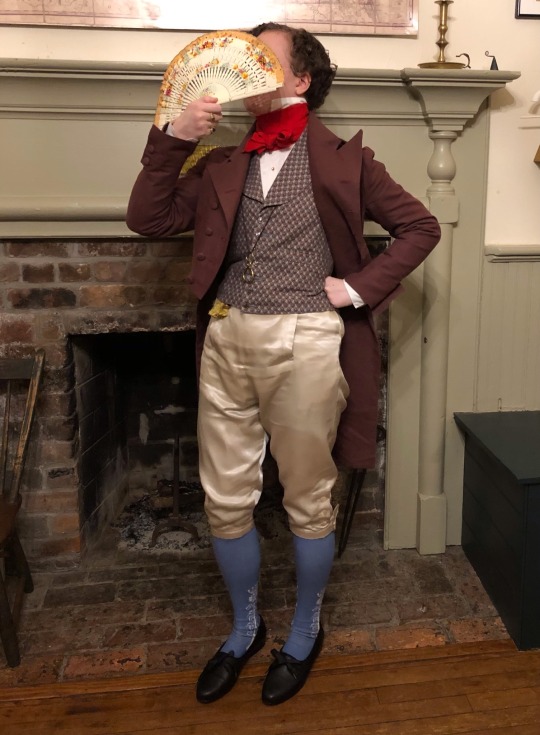



A happy new year to all!
New breeches and a new waistcoat I made. The waistcoat I’m particularly proud of as I drafted it from an original 1820s tailoring book. The fabric is a reproduction 1840-1860 print. I’m still tweaking how I construct breeches.
#historical fashion#regency#1820s’ men’s fashion#menswear#regency fashion#my post#sewing#fashion#miwackulous tye monday
121 notes
·
View notes
