#Public Health
Text
"The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) finalized a rule Tuesday [April 9, 2024] that will require 218 chemical plants to reduce toxic and carcinogenic airborne pollutants, aiming to reduce the number of people with elevated cancer risk by 96% nationwide.
The rulings principally address chloroprene: used to make rubber products, and ethylene oxide, used primarily for sterilizing medical supplies. Long-term exposure to these chemicals and their manufacturing have been identified as possible carcinogens, or cancer-causing agents.
According to a report in the Washington Post, this can include lymphoma, leukemia, breast cancer, and liver cancer.
Across a strip of Louisiana and Texas where half of the 218 chemical manufacturing facilities set to be affected by the new regulations are located, cancer rates of these kinds are substantially higher than national averages, leading it to be colloquially called “Cancer Alley.”
EPA Administrator Michael Regan visited Cancer Alley during the open-comment period of the proposed ruling, and said that across the 85 miles dotted with communities, he failed to meet a single person who didn’t know a loved one or friend who had either developed cancer, died of it, or knew someone who had.
Once implemented, the ruling will reduce more than 6,200 tons of toxic air pollution each year, according to the Post."
-via Good News Network, April 15, 2024
#I was going to say “wait isn't it normal for everyone to know someone who got cancer”#then I remembered that I grew up three miles from the site of a gigantic nuclear meltdown#which hardly anyone knows about it because they fucking covered it up btw#so it's possible I'm wrong and that is not a normal thing#united states#epa#environmental protection agency#louisiana#texas#cancer#cw cancer#public health#pollution#air pollution#environmental racism#environmental justice#oncology#good news#hope#cancer alley
297 notes
·
View notes
Text


Source

Source
Long overdue
#environment#health#public health#capitalism#news#current events#Joe Biden#politics#us politics#government#the left
114 notes
·
View notes
Text

NBC News CNN
21K notes
·
View notes
Text


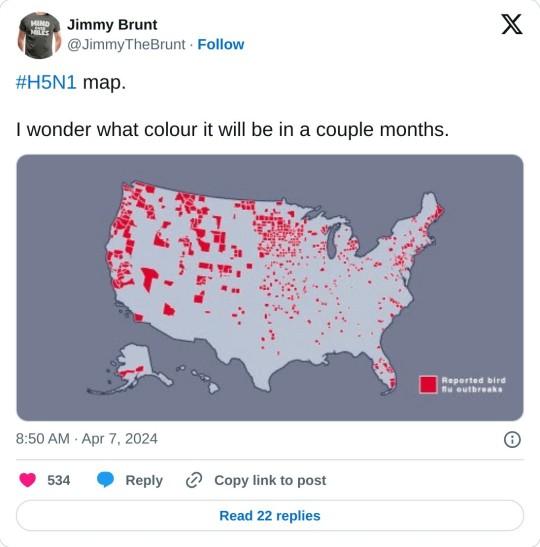
"If a pig catches both a human influenza A virus and an avian influenza A virus at the same time, it can spark a process known as viral reassortment — a genetic exchange in which flu viruses swap gene segments."
"Those swaps can introduce dramatic changes, producing a new virus with certain properties of a non-human strain coupled with the capacity to infect and spread between people."
"The death rate in humans may be upwards of 50 per cent, World Health Organization data suggests, though it's possible that milder infections are getting missed, skewing the case fatality ratio. Still, in a population that's never been exposed, the global impacts could be dire."
"More human cases could also be happening under the radar among farm workers who've moved to the U.S. from abroad, don't speak English as their first language, and may be hesitant to seek medical help, he added."
"So I think there's probably underreporting on both sides," Armstrong said."
"If [H5N1] gets into a population where there's constantly animals going in and out … it might not ever leave."
I've been watching this develop for the past several days, and apart from being terrified most people will not take this seriously (I've seen a handful of people already shout conspiracy on social media and it's alarming to see, as always). What I wanted to point out is that pandemics are going to continue to be our 'normal.' I watched a great video on YouTube a while ago (I believe it was by Vice?) that touched base on how this is going to become our new reality because of multiple factors (such as our proximity to animals, and environments/etc). It was when Covid hit and they did a piece debunking some of the misinformation floating on the internet. If I can find it I will post it here because it was informative and relevant to pretty much any world crisis we will see around any virus that spreads among a human population.
This post isn't trying to fear monger anyone, I just hope more people are aware of what is happening because this is important to talk about. There are already cases (of cows getting this bird flu) in the US, and I won't be surprised if there will be instances in more countries around the world. As usual, keep washing your hands/keeping good hygiene practices, masking up (and if you aren't I hope you consider it), and taking precautions if you do happen to visit/work or go near a pig or poultry farm too:
I'll keep track of this here of course, but please stay informed folks. And also FU to any governments who will try to minimize this or try to diminish the severity until it's too late and community spread happens like Covid because their actions are influenced by capitalistic interests.
Update (April 7th, 2024, 9:32pm EST): to anyone wondering where some of the source information originates from -here is a link to the CDC. They are tracking documented avian virus outbreaks in the US and the public can access it here:
#current news#current events#global news#united states#cattle#cows#cattle farming#avian flu#bird flu#h5n1#mask up#pandemic#covid#covid isn't over#covid conscious#covid is airborne#covid is not over#viruses#fuck capitalism#anti captialism#healthcare#public health#world health organization#cdc#news update#update
15K notes
·
View notes
Text
know someone who enjoys horror stories? share this one! it's true!
hahahahahahahahahaha aarrggghhhhhhhhhh
3,000,000 deaths due to COVID-19 last year. Globally. Three million.
Case rates higher than 90% of the rest of the pandemic.
The reason people are still worried about COVID is because it has a way of quietly fucking up your body. And the risk is cumulative.
I'm going to say that again: the risk is cumulative.
It's not just that a lot of people get bad long-term effects from it. One in seven or so? Enough that it's kind of the Russian Roulette of diseases.
It's also that the more times you get it, the higher that risk becomes. Like if each time you survived Russian Roulette, the empty chamber was removed from the gun entirely.
The worst part is that, psychologically, we have the absolute opposite reaction. If we survive something with no ill effects, we assume it's pretty safe.
It is really, really hard to override that sense of, "Ok, well, I got it and now I probably have a lot of immunity and also it wasn't that bad."
It is not a respiratory disease. Airborne, yes. Respiratory disease, no: not a cold, not a flu, not RSV.
Like measles (or maybe chickenpox?), it starts with respiratory symptoms. And then it moves to other parts of your body.
It seems to target the lungs, the digestive system, the heart, and the brain the most.
It also hits the immune system really hard - a lot of people are suddenly more susceptible to completely unrelated viruses.
People get brain fog, migraines, forget things they used to know.
(I really, really hate that it can cross the blood-brain barrier. NOTHING SHOULD EVER CROSS THE BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER IT IS THERE FOR A REASON.)
Anecdotal examples of this shit are horrifying. I've seen people talk about coworkers who've had COVID five or more times, and now their work... just often doesn't make sense?
They send emails that say things like, "Sorry, I didn't mean Los Angeles, I meant Los Angeles."
Or they insist they've never heard of some project that they were actually in charge of a year or two before.
Or their work is just kind of falling apart, and they don't seem to be aware of it.
People talk about how they don't want to get the person in trouble, so their team just works around it.
Or they describe neighbors and relatives who had COVID repeatedly, were nearly hospitalized, talked about how incredibly sick they felt at the time... and now swear they've only had it once and it wasn't bad, they barely even noticed it.
(As someone who lived with severe dissociation for most of my life, this is a genuinely terrifying idea to me. I've already spent my whole life being like, "but what if I told them that already? but what if I did do that? what if that did happen to me and I just don't remember?")
One of its known effects in the brain is to increase impulsivity and risk-taking, which is real fucking convenient honestly. What a fantastic fucking mutation. So happy for it on that one. Yes, please make it seem less important to wear a mask and get vaccinated. I'm not screaming internally at all now.

I saw a tweet from someone last year whose family hadn't had COVID yet, who were still masking in public, including school.
She said that her son was no kind of an athlete. Solidly bottom middle of the pack in gym.
And suddenly, this year, he was absolutely blowing past all the other kids who had to run the mile.
He wasn't running any faster. His times weren't fantastic or anything. It's just that the rest of the kids were worse than him now. For some reason.
I think about that a lot.
(Like my incredibly active six-year-old getting a cold, and suddenly developing post-viral asthma that looked like pneumonia.
He went back to school the day before yesterday, after being home for a month and using preventative inhalers for almost week.
He told me that it was GREAT - except that he couldn't run as much at recess, because he immediately got really tired.
Like how I went outside with him to do some yard work and felt like my body couldn't figure out how to increase breathing and heart rate.
I wasn't physically out of breath, but I felt like I was out of breath. That COVID feeling people describe, of "I'm not getting enough air." Except that I didn't have that problem when I had COVID.)
Some people don't observe any long (or medium) term side effects after they have it.
But researchers have found viral reservoirs of COVID-19 in everyone they've studied who had it.
It just seems to hang out, dormant, for... well, longer than we've had an opportunity to observe it, so far.
(I definitely watched that literal horror movie. I think that's an entire genre. The alien dormant under ice in the Arctic.)
(oh hey I don't like that either!!!!!!!!!)
All of which is to explain why we should still care about avoiding it, and how it manages to still cause excess deaths.
Measuring excess deaths has been a standard tool in public health for a long time.
We know how many people usually die from all different causes, every year. So we can tell if, for example, deaths from heart disease have gone way up in the past three years, and look for reasons.
Those are excess deaths: deaths that, four years ago, would not have happened.
During the pandemic, excess death rates have been a really important tool. For all sorts of reasons. Like, sometimes people die from COVID without ever getting tested, and the official cause is listed as something else because nobody knows they had COVID.
But also, people are dying from cardiovascular illness much younger now.
People are having strokes and heart attacks younger, and more often, than they did before the pandemic started.
COVID causes a lot of problems. And some of those problems kill people. And some of them make it easier for other things to kill us. Lung damage from COVID leading to lungs collapsing, or to pneumonia, or to a pulmonary embolism, for example.
The Economist built a machine-learning model with a 95% confidence interval that gauges excess death statistics around the world, to tell them what the true toll of the ongoing COVID pandemic has been so far.
Total excess deaths globally in 2023: Three million.
3,000,000.
Official COVID-19 deaths globally so far: Seven million. 7,000,000.
Total excess deaths during COVID so far: Thirty-five point two million. 35,200,000.
Five times as many.
That's bad.
I don't like that at all.
I'm glad last year was less than a tenth of that. I'm not particularly confident about that continuing, though, because last year we started a period of really high COVID transmission. Case rates higher than 90% of the rest of the pandemic.
Here's their data, and charts you can play with, and links to detailed information on how they did all of this:
Here's a non-paywalled link to it:
https://archive.vn/2024.01.26-012536/https://www.economist.com/graphic-detail/coronavirus-excess-deaths-estimates
Oh: here's a link to where you can buy comfy, effective N95 masks in all sizes:
Those ones are about a buck each after shipping - about $30 for a box of 30. They also have sample packs for a dollar, so you can try a couple of different sizes and styles.
You can wear an N95 mask for about 40 total hours before the effectiveness really drops, so that's like a dollar for a week of wear.
They're also family-owned and have cat-shaped masks and I really love them.
These ones are cuter and in a much wider range of colors, prints, and styles, but they're also more expensive; they range from $1.80 to $3 for a mask. ($18-$30 for a box of ten.)
#covid isn't over#covid 19#disability rights#disability advocacy#wear a mask#covid conscious#covid cautious#mask up#wall of words#public health#health care
7K notes
·
View notes
Text

It’s cold/flu/covid season again, please wear your goddam masks and get vaccinated if you’re able to
3K notes
·
View notes
Text

3K notes
·
View notes
Text
If you live in the U.S. and you’re 12+, you’re eligible for the updated bivalent anti-omicron booster shot, and it should be available in your local pharmacy.
Please reblog this post, as there’s been very little news coverage and shockingly little propagation of information about the availability of updated boosters.
#covid#COVID-19#boosters#booster shot#covid19#covid vaccine#Omicron#covid booster#bivalent vaccine#cdc#public health#epidemic#vaccine#vaccines#united states#moderna#pfizer#stay safe#vaccine booster#sars-cov-2#shot
35K notes
·
View notes
Text
what’s really ironic about the “just let everyone get infected w covid!! herd immunity!!” arguments now is that letting the virus run rampant through the world has actually achieved the opposite: everyone may get infected, but then they’ll just keep getting infected. delta infections didn’t protect against the original omicron variant. omicron BA.1 doesn’t protect you against BA.2.12.1. none of them really protect you against BA.4 and BA.5. mass infection is not going to create mass immunity, it just means that with every infection you’re rolling the dice on what this unpredictable and very creative virus is going to do to you
#play stupid games (encourage mass infection) win stupid prizes (mass infection... w indefinite reruns)!!!#covidposting at work again bc it really never changes (except for the worse)#don't even get me started on the ppl who originally were just lambasting the herd immunity crowd but now seem totally fine w it#bc 'vAcCiNEs pRoTeCt aGaiNsT sEveRe dIsEaSE' well maybe i don't want to take that risk!!#maybe i don't want to see what an infection will do to me! but thanks for fucking around so that i can find out ://#coronavirus#covid19#public health#skravler
25K notes
·
View notes
Text
A study conducted by the B.C. Centre for Disease Control has found that prescribing medical-grade opioids dramatically reduced the rates of deaths and overdoses for drug users living in B.C.
The study, published in the British Medical Journal, is described as "the first known instance of a North American province or state providing clinical guidance to physicians and nurse practitioners for prescribing pharmaceutical alternatives to patients at risk of death from the toxic drug supply."
Researchers looked at anonymized health-care data of 5,882 people between March 2020 and August 2021, all of whom had opioid or stimulant use disorder.
Those individuals filled a prescription under the B.C. Risk Mitigation Guide — clinical guidance developed in March 2020 to allow for physical distancing during the COVID-19 pandemic, and to reduce deaths through harm reduction.
Continue Reading
Tagging @politicsofcanada
#cdnpoli#canada#canadian politics#canadian news#british columbia#public health#harm reduction#drug usage#harm reduction works#overdose#research
1K notes
·
View notes
Note
Sorry I'm kind of dissociated and my vocab crashes during that can you explain the Biden drug thing in just. Shorter simple sentences.
Sure! You're not the only one who's mentioned being unclear on what it means either, and I'm happy to help
(Context for anyone else: US Sets Policy to Seize Patents of Government-Funded Drugs if Price Deemed Too High, via Good News Network, December 11, 2023)
From the very basics:
When drug companies create new drugs, they get a legal protection called a "patent." The patent means no one else can make or sell the same drug for whatever number of years.
Usually, this is about 10 years after the drug starts being sold to the public.
So, for those years, that one drug company is the only source of whatever medication. And since people need their medication, drug companies can charge however much money they want.
Meaning a lot of drugs that people need to live cost way too much money to buy.
So, with this, Biden told drug companies "Fuck you, if you keep making medicine too $$$ for people to afford, I'm giving your competition the right to make and sell those drugs too."
The US has never done anything like this before.
This is a huge threat to the whole (awful) drug industry in the US. It will save people thousands of dollars. If he does this, it will save lives.
--
Edit 12/17/23: Quick note, as people have said in the notes, this only applies to drugs made in part using taxpayer money. Which is! Literally all of them!
#Anonymous#prescription drugs#medicine#public health#biden#biden administration#united states#us politics#ask#me#good news#hope
13K notes
·
View notes
Text

Source
For context, 1/4 of Gaza’s 2 million population is 500,000. All 100% preventable.
#Gaza#Palestine#free Palestine#Israel#international politics#news#health#public health#current events
11K notes
·
View notes
Text







#human rights#palestine#Israel#water#water is life#gaza genocide#free palestine#free gaza#genocide#ethnic cleansing#ceasefire#ceasefire now#starvation#public health
791 notes
·
View notes
Text

We need climate action.
Digital illustration of a blonde woman wearing a mask facing the New York City skyline. She is standing on a fire-escape wearing a tan dress that reads, ‘climate change is a public health crisis.’
#art#feminism#feminist#illustration#climate change#clean air#wildfire#canada wildfires#air quality#climate action#climate crisis#public health#environmental justice
2K notes
·
View notes
Text
You might be forgiven for thinking it’s been a very quiet few months for the Covid-19 pandemic. Besides the rollout of new boosters, the coronavirus has largely slipped out of the headlines. But the virus is on the move. Viral levels in wastewater are similar to what they were during the first two waves of the pandemic. Recent coverage of the so-called Pirola variant, which is acknowledged to have “an alarming number of mutations,” led with the headline “Yes, There’s a New Covid Variant. No, You Shouldn’t Panic.”
Even if you haven’t heard much about the new strain of the coronavirus, being told not to panic might induce déjà vu. In late 2021, as the Omicron variant was making its way to the United States, Anthony Fauci told the public that it was “nothing to panic about” and that “we should not be freaking out.” Ashish Jha, the Biden administration’s former Covid czar, also cautioned against undue alarm over Omicron BA.1, claiming that there was “absolutely no reason to panic.” This is a telling claim, given what was to follow—the six weeks of the Omicron BA.1 wave led to hundreds of thousands of deaths in a matter of weeks, a mortality event unprecedented in the history of the republic.
Indeed, experts have been offering the public advice about how to feel about Covid-19 since January 2020, when New York Times columnist Farhad Manjoo opined, “Panic will hurt us far more than it’ll help.” That same week, Zeke Emanuel—a former health adviser to the Obama administration, latterly an adviser to the Biden administration—said Americans should “stop panicking and being hysterical.… We are having a little too much [sic] histrionics about this.”
This concern about public panic has been a leitmotif of the Covid-19 pandemic, even earning itself a name (“elite panic”) among some scholars. But if there’s one thing we’ve learned, three and a half years into the current crisis, it’s that—contrary to what the movies taught us—pandemics don’t automatically spawn terror-stricken stampedes in the streets. Media and public health coverage have a strong hand in shaping public response and can—under the wrong circumstances—promote indifference, incaution, and even apathy. A very visible example of this was the sharp drop in the number of people masking after the CDC revised its guidelines in 2021, recommending that masking was not necessary for the vaccinated (from 90 percent in May to 53 percent in September).
As that example suggests, emphasizing the message “don’t panic” puts the cart before the horse unless tangible measures are being taken to prevent panic-worthy outcomes. And indeed, these repeated assurances against panic have arguably also preempted a more vigorous and urgent public health response—as well as perversely increasing public acceptance of the risks posed by coronavirus infection and the unchecked transmission of the virus. This “moral calm”—a sort of manufactured consent—impedes risk mitigation by promoting the underestimation of a threat. Soothing public messaging during disasters can often lead to an increased death toll: Tragically, false reassurance contributed to mortality in both the attacks on the World Trade Center and the sinking of the Titanic.
But at a deeper level, this emphasis on public sentiment has contributed to confusion about the meaning of the term “pandemic.” A pandemic is an epidemiological term, and the meaning is quite specific—pandemics are global and unpredictable in their trajectory; endemic diseases are local and predictable. Despite the end of the Public Health Emergency in May, Covid-19 remains a pandemic, by definition. Yet some experts and public figures have uncritically advanced the idea that if the public appears to be tired, bored, or noncompliant with public health measures, then the pandemic must be over.
But pandemics are impervious to ratings; they cannot be canceled or publicly shamed. History is replete with examples of pandemics that blazed for decades, sometimes smoldering for years before flaring up again into catastrophe. The Black Death (1346–1353 AD), the Antonine Plague (165–180 AD), and the Plague of Justinian (541–549 AD), pandemics all, lacked the quick resolution of the 1918 influenza pandemic. A pandemic cannot tell when the news cycle has moved on.
Yet this misperception—that pandemics can be ended by human fiat—has had remarkable staying power during the current crisis. In November 2021, the former Obama administration official Juliette Kayyem claimed that the pandemic response needed to be ended politically, with Americans getting “nudged into the recovery phase” by officials. It is fortunate that Kayyem’s words were not heeded—the Omicron wave arrived in the US just weeks after her article ran—but her basic premise has informed Biden’s pandemic policy ever since.
Perhaps even less responsibly, the physician Steven Phillips has called for “new courageous ‘accept exposure’ policies”—asserting that incautious behavior by Americans would be the true signal of the end of the pandemic. In an essay for Time this January, Phillips wrote: “Here’s my proposed definition: the country will not fully emerge from the Covid-19 pandemic until most people in our diverse nation accept the risk and consequences of exposure to a ubiquitous SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes Covid-19.”
This claim—that more disease risk and contagion means the end of a disease event—runs contrary to the science. Many have claimed that widespread SARS-CoV-2 infections will lead to increasingly mild disease that poses fewer concerns for an increasingly vaccinated (or previously infected) population. In fact, more disease spread means faster evolution for SARS-CoV-2, and greater risks for public health. As we (A.C. and collaborators) and others have pointed out, rapid evolution creates the risk of novel variants with unpredictable severity. It also threatens the means that we have to prevent and treat Covid-19: monoclonal antibody treatments no longer work, Paxlovid is showing signs of viral resistance, and booster strategy is complicated by viral evolution of resistance to vaccines.
But these efforts to manage and direct public feelings are not just more magical thinking; they are specifically intended to promote a return to pre-pandemic patterns of work and consumption. This motive was articulated explicitly in a McKinsey white paper from March 2022, which put forward the invented concept of “economic endemicity”—defined as occurring when “epidemiology substantially decouples from economic activity.” The “Urgency of Normal” movement similarly used an emotional message (that an “urgent return to fully normal life and schooling” is needed to “protect” children) to advocate for the near-total abandonment of disease containment measures. But in the absence of disease control measures, a rebound of economic activity can only lead to a rebound of disease. (This outcome was predicted by a team that was led by one of the authors [A.C.] in the spring of 2021.)
A pandemic is a public health crisis, not a public relations crisis. Conflating the spread of a disease with the way people feel about responding to that spread is deeply illogical—yet a great deal of the Biden administration’s management of Covid-19 has rested on this confusion. Joe Biden amplified this mistaken perspective last September when he noted that the pandemic was “over”—and then backed that claim by stating, “If you notice, no one’s wearing masks. Everybody seems to be in pretty good shape.” The presence or absence of health behaviors reveals little about a threat to health itself, of course—and a decline in mask use has been shaped, in part, by the Biden administration’s waning support for masking.
Separately, long Covid poses an ongoing threat both at an individual and a public health level. If our increasingly relaxed attitude toward public health measures and the relatively unchecked spread of the virus continue, most people will get Covid at least once a year; one in five infections leads to long Covid. Although it’s not talked about a lot, anyone can get long Covid; vaccines reduce this risk, but only modestly. This math gets really ugly.
The situation we are in today was predictable. It was predictable that the virus would rapidly evolve to evade the immune system, that natural immunity would wane quickly and unevenly in the population, that a vaccine-only strategy would not be sufficient to control widespread Covid-19 transmission through herd immunity, and that reopening too quickly would lead to a variant-driven rebound. All of these unfortunate outcomes were predicted in peer-reviewed literature in 2020–21 by a team led by one of the authors (A.C.), even though the soothing public messaging at the time called it very differently.
As should now be very clear, we cannot manifest our way to a good outcome. Concrete interventions are required—including improvements in air quality and other measures aimed at limiting spread in public buildings, more research into vaccine boosting strategy, and investments in next-generation prophylactics and treatments. Rather than damping down panic, public health messaging needs to discuss risks honestly and focus on reducing spread. Despite messages to the contrary, our situation remains unstable, because the virus continues to evolve rapidly, and vaccines alone cannot slow this evolution.
In the early months of the pandemic, many in the media drew parallels between the public’s response to Covid-19 and the well-known “stages of grief”: denial, bargaining, anger, depression, and acceptance. The current situation with Covid-19 calls for solutions, not a grieving process that should be hustled along to the final stage of acceptance.
833 notes
·
View notes
