#Nature ecology evolution
Text
Okay, so this is really cool! You have this phenomenon where some plants grow edible appendages to their seeds to entice ants to carry them underground where they can safely sprout. And then you have wasps which lay their eggs on the leaves, stems, and other parts of plants and trigger the growth of galls (swellings) which both feed and protect the wasp larvae until they reach maturity.
The boy who was watching the ants noticed they were taking wasp galls underground, too. Further exploration found that the wasp larvae were unharmed inside the galls; the only thing the ants had eaten were edible appendages similar to those on the seeds they collected. The wasp larvae stayed safe inside the ant nest, feeding on their galls, until it was time to emerge and head back out to the surface.
So it turns out that the edible portions of the galls have the same sorts of fatty acids as the edible parts of the seeds. And those fatty acids are also found in dead insects. Scientists think that the wasps evolved a way to make the galls they created mimic the edible portions of the seeds to get the ants to collect the galls. This isn't the only example of wasps making use of ants as caretakers for their young, but it's a really fascinating example thereof--especially if you consider ants evolved from wasps at least 100 million years ago.
#wasps#ants#plants#galls#oak galls#insects#invertebrates#Hymenoptera#ecology#bugs#animals#wildlife#nature#trees#entomology#science#natural science#evolution#animal behavior
12K notes
·
View notes
Note
I heard that sharks and rays are super closely related. Are skates an approximate bridging “group” between them? Or are they outside of both groups
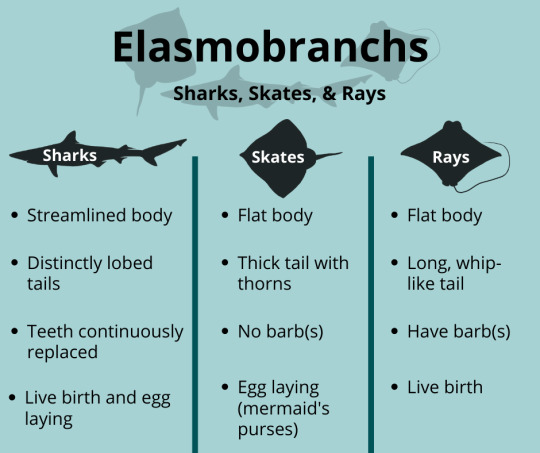
They are all really closely related- there in all the same class known as Chondrichthyes, or cartilaginous fish. Sharks evolved first, approximately 350 million years ago during the Carboniferous period. Skates and ray came around at approximately the same time as each other 150 million years ago during the Jurassic period.
So skates aren't really a "bridging group", they're actually most closely related to rays!
#marine biology#marine ecology#animals#science#biology#animal facts#wildlife#marine life#ocean#fun facts#shark#sharks#rays#sting rays#skates#evolution#zoology#fossils#natural history#jurassic period#carboniferous#sea life#sea creatures#marine animals#fish#chondrichthyes
592 notes
·
View notes
Text
So, I've decided to start learning biology.
My education left me with only primary school biology knowledge, because I had zero biology lessons in high school, and now I find myself sorely lacking in knowledge. Which is inconvenient, now that I'm sick and have no idea what to do. I didn't know where to start, but my roommate is in high school right now, and I borrowed her biology textbook to get myself started.
The biology textbook was so misinformed and outdated it made me worry for the education system. Not only they didn't update any info from the last 40 years, some of the info was completely wrong. For instance, it claims there's 6 billion people on the planet (there's 8), and that there's 6 empires of all living things (there's 8, and some of the old ones have been renamed and disputed). I learned quickly to fact-check every bit of information on wikipedia, and this is where I found some truly astounding info that I had no idea about.
If you all have learned this in highschool and it's common knowledge, please excuse me, but I am shocked.
One of the first topics the book covers is evolutionary history of the planet, and it explains how blue-green algae were the first historic plants to produce a lot of oxygen, which sounds like a positive development for us, because most of the living things right now thrive on oxygen. But, looking it up wikipedia uncovered that it was in fact, an extinction event. Most of life on earth was at that point, thriving in non-oxygen environment, and the introduction of oxygen killed 85% of all living species on earth. It was a huge disaster that happened! It's called 'Great Oxidation Event', or the 'Oxygen Catastrophe'.
But that's not all, I found out that it was not only that which destroyed almost all life on earth, but there's been 5 different events in the history that destroyed close to 80% of all species on the planet, and for some of them we don't even know why. We only found proof that lots of species disappeared at all times and the dominant species on the planet rapidly changed, but no idea why, for some of them it's assumed it has to do with volcanoes or ice, and of them that is well known is the meteor, that ended the big dinosaurs.
I never realized how much of evolution was destruction and then starting over, this was shocking to me. It was also fascinating, I found myself following links and learning more about extinction events, also that we're currently in the extinction event caused by humans who are driving lots of species into extinction by taking over their habitats, which made me sad.
At this point I started reading other, biology-related materials, for example, I read a book named 'What an Owl Knows', which is written by Jennifer Ackerman, an owl scientist who studied owls her entire life; now I know more about owls. I also started listening to an audio book about the ocean, and this one proved to be very difficult to follow, but I'll tell you what I learned from both.
The owl book was charming, I found out that owls are the most quiet, soundless birds when they fly, because their wings and feathers are the biggest part of their bodies. This is how they manage to swoop up prey without anyone hearing a single flap. They're also very silent and subtle. Unless you're studying owls, you won't be able to tell if the owl is startled, or scared, because she will sit very still and not give you any clues. Smaller owls can go into their 'freeze' response easily if they're being hunted, because their instinct is to be still and not move when in danger! It can make you feel like the owl is not scared, since she's not moving, but she is most likely not comfortable if anyone is approaching her.
Owls have similar faces to our faces, and they're very charismatic to us; this is why baby owls, and injured owls in human care, can sometimes imprint on humans. This is bad news for the owls, because once it happens, they can never again be released into the wild, they'll either never learn to hunt, or they'll act towards humans, like they do to other owls - brawling, attacking, aggressive, territorial. Even if they really like us, they will keep acting like we're other owl, not a different species. They see us similarly to how we see them.
One of the best information I've learned, is that in Serbia, there's the biggest gathering of owls of all species, there can be more than 300 owls in one place at the time. The reason for this is common use of old-fashined methods of harvesting grains, which leaves a lot of leftover corn and wheat on the ground, attracting mice, rats, and other small rodents, which creates a great food source for owls. Serbian farmers don't use rodenticide, so owls don't get poisoned. Owls so beloved and appreciated there, that they have an owl festival every year, and the whole month of november is called 'Sovember', because owl in serbian is 'sova'. I never knew about this, even though it's my neighbour country! I looked this up, and I found a website for the international owl festival, but I couldn't find any more info. I would appreciate it so much if any serbian followers could write me about this and tell me their experiences with it, I've never wanted to visit Serbia more!
The book contains information about owls used in Harry Potter movies, including the names of the owls, as well as discussing how the books made owls popular, and how it made people want them as pets. Owls do not make good pets, because they're predators and will destroy things and be very difficult to care for, but the book encourages readers to find the local owls and keep them safe, to leave old trees with holes in them standing, so the owls could nest in them, or to hang up baskets that can also be used as nests. It was a lovely, charming book and I recommend it to anyone who wants to know more about owls.
The ocean book is named 'How the Ocean Works', by Helen Czerski, and I haven't finished yet, but it opened up a lot of questions for me. The funniest part of it was the breakup of what people used to think about the ocean; apparently before research, people assumed that the sea is salty because it's been left in the sun for too long, and that's just what you get from sun exposure, they believed that deep down it was not salty anymore. They also believed that the sea water cannot go putrid if left standing. It took a scientist checking this to confirm it was not true; sea water did go putrid left in a bucket in the sun, and non-salty water did not turn salty when left in the sun for months. It was interesting to know that for the longest time, people didn't realize it was the salt in the sea that made it salty, I then wondered how they got salt, and it turns out they just got it from the salt mines, which are leftover from the long-dried up seas.
Now new information that I didn't know, was that the salinity is different between the oceans, the Atlantic is saltier than the rest. The book also explained about how the salt is connected to the currents, and to the movements of the sea, and also changes the density of the water. One thing that had me taken aback was that the ocean waves are not only caused by the wind, but the water is reacting to earth's rotation, and this rotation is constantly moving the water. It feels like the ocean is being pulled both by the earth and the moon, constantly being driven by planetary forces, which is interesting, because it's difficult to tell that just by looking.
The book calls ocean the 'blue machine', because it's always moving, and filled with energy. Sun is always warming up the surface, making it a great reservoir of solar energy, and the book goes on about how it's possible to harvest this energy, using hot water, and cold water, apparently there's already buildings being cooled down by the ocean power, but I never managed to figure out how! I tried looking it up, and also found nothing. I wish the book explained the physics of it, so that I could try it out, it's a great thing to be able to get power jut by using hot and cold water, and the water is already heated by the sun, while you can get cold water from the bottom of the sea.
I think I might understand this book better if I read it, rather than listening to the audiobook, which as you can see, just has me puzzled because I do not catch details. Still I wanted to share my new learnings, and ask if anyone can tell me more, or if this is all knowledge that people who had biology in high school already have. I'm having a great time learning, especially because I can just divert in any direction that has my interest, and I can seek out information that gives me useful, practical knowledge. Wish all learning processes could be free and inspired like this!
#biology#owls#ocean#evolution#extinction#learning biology#making up for lack of high school knowledge#information#resources#natural power#harvesting power from nature#ecology#international owl festival#serbia
77 notes
·
View notes
Text
i KNOW this is a bug blog but i wanna talk ab one of my fav guys ever.,.,
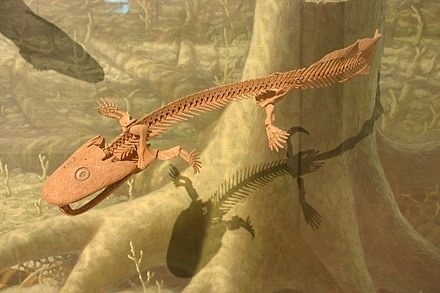


Acanthostega !!!
theyre SO goofy!! appeared in the late devonian, this freaaaky thing has EIGHT DIGITS PER HAND!!! it has limbs but CANNOT bear its own weight, stuck in the waater.
i just love these guys so much <33
#next post WILL be about isopods.#trust!!#ecology#prehistoric#natural history#evolution#paleontology#fossil#acanthostega#devonian
110 notes
·
View notes
Text

Queering the Wild by Micha Rahder (2019) [final]
Queer Intimacy in Non-Human Animals
The author introduces several examples of ‘queerness’ across the animal kingdom—the ‘birds and the bees’, --a lot about birds since we have a lot of research on them. The study on zebra finches reminded me of the concept of ‘naturecultures’; they choose their mates and often do not stray, same-sex or otherwise and so this supports the idea that there is more to ‘bird life than breeding and that the social aspects of bonding might be just as important’ (02).
“The idea that sexual activity might be about more than just making babies is hard for people who were raised in contemporary U.S. American culture in particular, with its focus on abstinence-only sex ed and heavy legislation of uteruses and the people who have them” (02) but finches, bonobos, dolphins or ‘female fish that prefer males that have had sex with other males, all chip away at that anthropocentric frame’ (02).
“Because scientists carry their cultural biases into their work, most research approaches these kinds of queer traits and behaviors as problems to be solved” (02). Heteronormativity has made scientists ‘run in circles’ trying to explain why such ‘maladaptive’, ‘perverted’ traits appear throughout the natural world such as nutritional deficiencies, the stress of captivity, that they’re just ‘dumb’ and can’t tell the difference, it’s a ‘misfire’ attempt at heterosexuality, or they’re just ‘practicing’.
“Evolutionary biologists need to think about same-sex sexual behavior in non-human animals as more than just a problem to be solved” and “same sex sexual behavior is both a trait that is potentially shaped by selection and a force that shapes selection on other traits” or they should “consider how same-sex sexual activities shape ongoing evolutionary processes” (03).

Extending Our Chosen Family
Evolution has no “direction or purpose” and humans are not “the representation of the ultimate expression of life on earth” (03). If we look at microbiology, we can see true diversity. “Only recently have scientists started to pay attention to how much [microbes exchanging DNA] might be driving evolution” (03). Fungi are also an incredible example of sexual diversity; with one species alone having more than 23,000 documented mating types (sexes) and individuals can physically ‘merge or separate in different environmental contexts’ making it difficult to differentiate them.
‘Symbiopoesis’ or “how organisms can be intimately involved in each other’s development” (squid and light emitting bacteria, bees and pollination, acacia trees and ants, wasps and figs).(03) Again this reminds me of the Lakota concept of Mitakuye Oyasin—we are all related, all my relatives.
Competition//Cooperation is another binary that queer ecology can challenge.
“Queering nature means learning about our connectedness with all the living earth. Here, the classic queer recognition of chosen family extends beyond humans, recognizing our kinship and interdependence with our companion animals, the foods we eat, our microbes and others. It means taking pleasure in those connections, learning to recognize pleasure in others and understanding how our human identities, gender expressions and sexual behaviors are only a small piece of the wide, queer living world” (04).
Queer ecology asks us to be curious about the ‘magnificent overabundance of reality’ (Bagemihl). “Breaking free from the historical biases of science allows us to move forward together with other life on earth, rather than thinking ourselves as separate from or above it. That kind of hierarchical thinking has kept queer and other marginalized communities away from the benefits of being outdoors and has led directly to the tangle of global environmental crises in which we find ourselves now. Learning from non-humans is a great way to undo these legacies” (04).

#queering the wild#queer ecology#queer nature#ecofeminism#heteronormativity#queer theory#critical ecology#environmental politics#ecology#queer history#mitakuye oyasin#evolution#naturecultures#Symbiopoesis
37 notes
·
View notes
Text
fun fact that bc of one of their claws being Obnoxiously Fucking Huge, male fiddler crabs literally can't eat with it. Which means they spend like twice as much time eating as females, since females can shovel food into their mouth with both claws but males can only do it with one
This relates to the concept of "honest/costly signaling" in ecology, which contains the idea that traits that attract mates can be an accurate display of an individual's fitness/capability due to said trait actually having disadvantages (ex. long attractive tails in some birds making moving more difficult, large claws making it harder to eat, being brightly colored making you more visible to predators, etc). The idea being that if certain attractive traits are actually disadvantageous, then an organism thriving and being overall healthy despite said traits is evidence that said organism is Good At Surviving, and therefore a good potential mate.
So while bigger claws do have the benefit of giving a male fiddler crab an edge in fights with other males, which play a big role in female mate choice, a male being healthy while having his bigass claw in the first place also serves as indirect proof that he's good at successfully obtaining enough food to survive
but like. look at this dude. he can't eat with that thing. he's got one functional food shovel bc the women think him having a one-purpose bigass muscle arm is Good Baby Material. and they're not even technically wrong

#crabs#ecology#nature#also this is part of why the common perception of ''evolution has to be strictly beneficial'' is wrong#evolution tends toward 'beneficial' but its more like. beneficial in the sense that it helps you get laid rather than helps you objectively#negative or dubiously helpful traits can get selected for if they help you mate#in some cases a problematic trait can actually show fitness in other areas and therefore get selected for#even a net negative can get populous if it doesn't kill you before you can mate#which is how you get stuff like that one extinct boar species whose tusks literally bored into their brains#also fiddler crabs are fun to watch then they do their little arm waving displays
366 notes
·
View notes
Text


#marine biology#marine biology shitpost#biology#studyblr#natural history#paleoblr#natural science#mental wellbeing#biologyblr#scientific illustration#entomology#sea creatures#sea life#ecology#deep sea#endangered species#fishblr#signal boost#classification#evolution#snailblr#seashells#malacology#chaotic academia#scienceblr#dark academia#shit post#taxonomy#special feature deep sea creature#indigenous
267 notes
·
View notes
Text

9/30(土)のトトロの森の秋の昆虫観察会、大学院で生態学を学んだ/学んでいる3人のガイドで、生物を目の前にする興奮と「進化」の面白さ、それを探る研究の魅力の紹介まで絡めた、一味違う観察会ができたのではないか、と手応えのある内容でした。カタツムリの右巻き/左巻きの進化もその一つ。
43 notes
·
View notes
Photo

The story of a conquest. The fruiting body of a parasitic fungus erupts from the body of its victim.
Attribution: Roberto García-Roa
BMC Ecology And Evolution Image Competition
#roberto garcia-roa#photographer#bmc ecology and evolution image competition#parasitic fungus#insect#nature
79 notes
·
View notes
Link
In our latest study published in Ecology and Evolution, we show that animals—in this case, bees—are also prone to being tricked into making poor decisions, which explains a lot about how gaps in perception are exploited in nature.
When Charles Darwin was testing the theory of evolution 150 years ago, he looked at the interaction between flowering plants and the animals that forage to collect nectar.
This helped establish that flowers have adaptations to promote easier pollinator access, making it beneficial for the animal who gets a food "reward" from them. At the same time, it means the plants get pollinated and can reproduce.
One perplexing problem is some flowering plants that reproduce by pollination are non-rewarding—the animal doesn't get nectar from visiting the flower. This is true of certain orchids, yet these flowers are still visited by pollinators and survive well in nature.
Continue Reading
129 notes
·
View notes
Text
Okay. This is a pretty big deal in the world of mycology. Historically fungi have been divided up into either parasites that siphon resources from plants, mutualists that cooperate with them, or saprotrophs that break down decaying organic matter (plant and otherwise.) The genus in question, Mycena, has traditionally been made of saprotrophic species feeding on decaying wood.
However, what scientists are observing is Mycena fungi displaying primitive mutualistic behaviors, specifically providing living plants with nitrogen and getting carbon in return from a living partner, or getting to chow down on the plant's remains once deceased. This shows a significant level of adaptability that hasn't been observed in fungi beforehand, though given how much we don't know about fungi there's a good possibility this isn't an unprecedented event.
It doesn't surprise me one bit that we're seeing this in Mycena. These fungi are especially opportunistic; in fact, that mushroom growing out of a frog's skin that we saw a while back was also a Mycena species. Perhaps we need to add bonnet mushrooms to raccoons, dandelions, and other hardy generalists as symbols of scrappy survival in spite of environmental pressures.
#Mycena#bonnet mushrooms#mushrooms#mushroom#fungi#fungus#mycelium#mycology#botany#biology#nature#science#scicomm#evolution#environment#ecology#mutualism#mycorrhizal fungi
193 notes
·
View notes
Text
Discovered fossils support the "Necks and Sex" theory in giraffes
Fossil discovery suggests that a giraffe's long neck evolved due to sexual selection (longer necks = greater reproductive success) rather than to reach food better.
Traditionally, it's believed that a giraffe's long neck is to help it reach more food. But this theory doesn't hold considering that giraffes don't always forage from the topmost leaves, and longer-necked giraffes don't survive better than shorter-necked counterparts during droughts.
This discovery show ancient giraffe skulls with a helmet-like structure to aid in fighting-which often happens between males for mates. It's neck bone structure also suggests adaptation to fighting, thus lending support for the theory that a giraffe's long neck might also be used for fighting rather than for foraging.
#aslzoology#asl zoology#zoology articles#zoology#evolution#giraffes#studyblr#ecology#nature#animals#stem#stemblr
122 notes
·
View notes
Text
“How did these tree-hopping furry angels evolve to be the cutest thing in the world, objectively speaking? They have saucer eyes, wet noses, chunky tails, toe claws, matriarchies, a feature film starring role, and all the mystery of 100 species spending millions of years on a remote island.” A ridiculously long introduction, but fascinating once it gets started.
Wildlife ecologist and official Lemurologist Dr. Lydia Greene.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

Freshwater mussels of the Illinois River.
#wip#graphicnonfiction#lakesenachwine#illinoisriverbluffs#illinois#illinois river#lowerillinois#illinoisrivervalley#illinoisriverbasin#illinoisnaturelovers#mississippiriverbasin#mississippiflyway#natural history#tallgrassprairie#ecology#geology#evolution#aquatic#home#floodplains#settler colonialism#alloppressionisconnected#cleanwater#waterforall#mussels#freshwatermussels
95 notes
·
View notes
Text

Guest Column: Queer Ecology
Author(s): TIMOTHY MORTON
Queer Ecology: 'Frankensteinian meme splice' between ecological criticism and queer theory. Foundations--ecology and queer theory both demand intimacies with other beings.
"Our era requires it--we are losing touch with a fantasy Nature (capitalized to emphasize that it is less natural than nature) that never really existed" while we are losing the very real life forms in Earth's sixth mass extinction event…
Judith Butler identified how heterosexist gender performance produces the binary--inside//outside. Ideologies of Nature , are founded on inside-outside structures that resemble the boundaries heterosexism polices
when the environment becomes intimate--as in our current age of ecological crisis--it is no longer an environment since it no longer just happens around us; this is the difference between weather and climate.
society once defined itself by excluding dirt, germs, pollution but this is impossible--we must know where our waste goes.
"excluding pollution is part of performing Nature as pristine, wild, immediate and pure" (274)
'science is too important to be left to scientists.'
nonessentialism- Darwin; evolution=lifeforms made of other lifeforms
deconstruction--no text or lifeform is one 100% 'authentic'
'queer theory and ecology supposed a multiplication of differences at as many levels and on as many scales as possible' 275 (reminds me of infinite diversity in infinite combinations...star trek)
'life is catastrophic, monstrous, non holistic, and dislocated, not organic, coherent, or authoritative'
'life-forms are liquid; positing them as separate is like putting a stick in a river and saying, 'this is river stage x' (reminds me of mni wiconi-water is life)
life forms constitute a mesh--that blurs all boundaries between species, living/nonliving, organisms and environment.
gender diversity and biodiversity are deeply intertwined. plants and animals are hermaphroditic before they are bisexual and are bisexual before they are heterosexual. males and females of most plants and half the animals can become hermaphrodites either together or in turn, and hermaphrodites can become male or female; many switch gender constantly.
the story of evolution is a story of diverse lifeforms cooperating with one another.
evolutionary satisficing--if your body kind of works, you can keep it. gender and DNA are both performative.
speciesism- underlied with sexism, racism and homophobia
any attempt at queer ecology must imagine ways of doing justice to life-forms while respecting the lesson of evolutionary biology--that the boundary between life and nonlife is thick and full of paradoxical entities. 276
the life//nonlife binary--there isn't a rigid, narrow boundary between the two. if a virus is alive, a devil's advocate might claim, so is a computer virus.
queer ecology might abandon the term 'animal' and adopt something like 'strange stranger' (arrivant)--irreducible, whose arrival cannot be predicted or accounted for (hospitality).
instead of reducing everything to sameness, ecological interdependence multiplies differences everywhere. unmysterious and miraculous. interdependence--it is the reason life exists at all
queer ecology questions the human//nonhuman binary.
queer ecology--go the end and show how beings exist precisely because they are nothing but relationality, deep down--for the love of matter.
every life form is familiar because we are related to it. we share DNA, cell structure, subroutines in the brain.
collectivity--consciously choosing coexistence
we shall achieve a radical ecological politics only by facing the difficulty of the strange stranger. (we have others--rather, others have us--literally under our skin (clark))
Against Compulsory Nature
to solve our environmental problem (like global warming) we should be working with intimacy.
darwin; the engine of sexual selection is sexual display. appearances and behaviors. sexuality=sheer aesthetic display
environmentalism-tries to rise above sexuality. Loving Nature becomes enslaved to masculine heteronormativity. a performance that erases the trace of performance--"leave no trace". masculinity is 'Natural'-'Natural' is Masculine. rugged, bleak, masculine Nature defined through contrasts; outdoorsy and extraverted, heterosexual, able-bodied. aggressively healthy, hostile to self-absorption. Not feminine, no room for irony or ambiguity, nonhumorus. Masculine Nature is afraid of its own shadow, afraid of subjectivity
Organicism wants Nature untouched, 'virgin', established by exclusion, then the exclusion of exclusion. Naturalized. queer ecology--interconnectedness is not organic. mythical Nature dissolves when we look directly at it.
'dark ecology'--zombie-like quality of interconnected lifeforms, keeps going and going and going like the undead
Frankenstein--queer ecological ethics might regard beings as people even when they aren't people.

vegetarian (vegan) rhetoric often obsessed with obsession, equating madness with crime, crime with disease: longing for a society without a trace--a society without people
Into the Wild novel--fatal experimentation with masculine Nature, realizes other people are important just before dying from a poisoness plant. he was not in as remote a location as he believed. his concept of wilderness overrode his survival instinct. they might think they are escaping civilization and its discontents but they actually act out its death instincts.
fantasize control and order; "i can make it on my own"--myth of self made man, editing out love, warmth, vulnerability and ambiguity.
Queer ecology must visualize the unbeautiful, the uncold, the 'lame', the unsplendid
joy as coexistance with coexistance
ecology and queer theory are intimate. its not that ecological thinking would benefit from an injection of queer theory from the outside. it's that, fully and properly, ecology is queer theory and queer theory is ecology: queer ecology.
#Guest Column: Queer Ecology#queer ecology#ecofeminism#queer theory#critical ecology#ecology#dark ecology#nature#environmental politics#heteronormativity#queer history#erotophobia#evolution#masculinity
7 notes
·
View notes
Photo

#'evolution seems to take delight in improbable exceptions to the rule'#also love this saying that platypuses didn't read our textbooks#my ecology professor is always saying that. that humans make categorical boxes for nature and species#and that species don't fit within them/do not conform to the boundaries we place#trek#library#life signs
12 notes
·
View notes