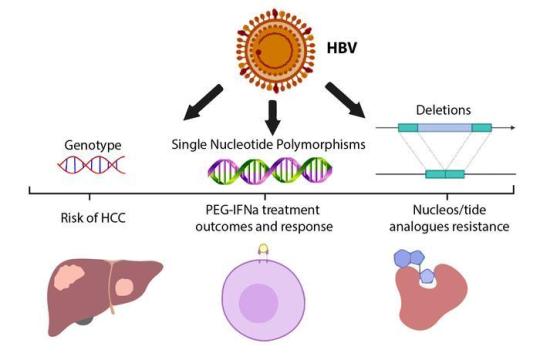
#Hepatitis B Virus
Text
Chronic Glomerulonephritis
Chronic Glomerulonephritis are a group of disorders in which the glomeruli are predominantly involved due to an inflammatory process which does not abate.
0 notes
Text
PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT OF BLOOD SCREENING ASSAYS: EARLY DYNAMICS OF HEPATITIS B VIRUS (HBV)-DNA AND SURFACE ANTIGEN (HBSAG) IN RAMP-UP PHASE OF VIREMIA
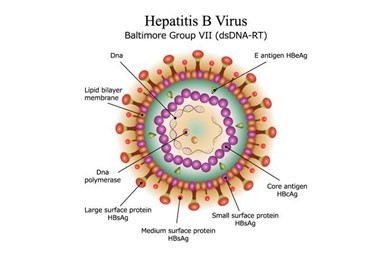
In a previous article, we discussed Hepatitis C, a serious liver disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV), and the dangers of HCV and HIV co-infection. Today's topic is Hepatitis B, which is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Hepatitis B is a viral infection that affects the liver and can cause both acute and chronic disease. Acute Hepatitis B can last for as little as six months. In its chronic form, the virus remains in the person's body for a longer period of time and goes untreated; it can endanger people's lives by causing cirrhosis, fibrosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, and end-stage liver disease.
Hepatitis B has no known cure. In some cases, the infection will resolve on its own (in 4 to 8 weeks for more than 9 out of 10 adults). Some adults who contract this virus as adults become "carriers," (a chronic condition) and are likely to infect others for the rest of their lives unknowingly. CHB patients must be treated for the rest of their lives. Early HBV exposure frequently results in chronic HBV and the virus's persistence due to the lack of cellular immune responses or strong antibodies.
HBV carriers may benefit from treatment that inhibits viral replication, boosts immune defences against the virus, or a combination of the two. The effectiveness of the treatments is entirely dependent on regular testing and monitoring of the various stages of the disease. One of the blood tests used to determine viral activity in an infected patient's body is the HBV DNA (viral load test).
The natural progression of chronic HBV infection can be divided into five stages, the last of which is seroconversion of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen. Hepatitis B is not detected in your blood at this stage, or hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) is negative or not detected in the blood.
Helvetica Health Care is a market leader in the provision of seroconversion panels and blood screening assays, which are critical in the monitoring and treatment of life-threatening diseases such as Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, and HIV. We hope that the information provided below will help you learn more about HBV and the dynamics of the Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)-DNA viral load test and Surface Antigen (HBsAg) in the Ramp-Up Phase of Viremia (the presence of virus in the blood).
WHAT IS THE HBV-DNA VIRAL LOAD TEST?
The viral load test, also known as hepatitis B virus DNA quantification, is a blood test that determines the amount of hepatitis B virus DNA in a chronically infected patient's blood. Viremia is typically measured in "international units per millilitre" (IU/mL); previously, it was measured in "copies per millilitre" (cp/ml). The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) technique is used for the test.
Other factors, such as Hepatitis B e-antigen (HBeAg) status, liver enzymes or serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST) or alanine aminotransferase (ALT) tests, and inflammation levels, must support the information gathered through this test. It is critical to monitor your plasma viral load on a regular basis in order to determine the stage of your infection. Several lab tests, including viral load, are used to determine the stage of the infection.
In chronic HBV infection, quantitative understanding of HBV dynamics influences drug treatment and immunotherapy timing. It can aid in the development of the best treatment plans for individual patients.
The five stages of Hepatitis B infection are
Immune tolerance,
Immune active,
Inactive HBV carrier state,
HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B, and
Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)-negative
Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is when hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) persists for six months or more. Most infected persons are unaware of their HBV infection and present advanced disease.
Annually, between 0·5% and 3% of inactive HBV carriers lose HBsAg. Spontaneous HBsAg clearance usually confers a good prognosis if there is no pre-existing hepatocellular carcinoma or cirrhosis at the time of HBsAg seroclearance (the clearance or removal of an antigen from the blood.) Following the loss of HBsAg, seroconversion to antibody against hepatitis B surface antigen (anti-HBs) is more likely to stop the development of cirrhosis and hepatocellular cancer, and it shows immunity to HBV and may suggest a better prognosis.
Throughout treatment, it is critical to monitor HBV DNA levels. Doctors detect HBV DNA when administering daily antiviral medications to see if the drug is lowering your viral load and to ensure that the antiviral is effective.
Testing of the International Standard and 10-30 seroconversion panels is required to demonstrate "state of the art" assay performance for detecting bloodborne viruses such as HBV. The evaluation of HBV-DNA and HBsAg assay performance is critical for understanding the dynamics of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)-DNA and Surface Antigen (HBsAg) in the Ramp-Up Phase of Viremia. According to research, the viral doubling duration in the ramp-up phase (period of exponential growth in viral load) is the same above and below the quantification limit of the viral load assay.
It is critical to avoid hepatitis B infection in order to reduce the risk of developing chronic disease or liver cancer. Regular testing that yields high-quality and accurate results is the only way to prevent disease. Ensuring high-quality test results is not only good for public health but also good for your lab's reputation.
HHC's QUALITY CONTROL PANELS can be used to test the sensitivity, specificity, and working range of your assays, as well as for diagnostic development and batch release in manufacturing. Panels include representative data from current market assays. Depending on the intended use of the panel, our VERIFICATION / VALIDATION Panels are designed to be used with assays to determine the presence of antigen, antibody, RNA, or DNA.
In addition, we have an extensive range of SEROCONVERSION PANELS for detecting asymptomatic donors infected with HIV, HCV, HBV and EBV, and SURVEILLANCE PANELS and LONGITUDINAL PANELS. Our panels are run on as many different diagnostic kits as possible to measure relevant markers of seroconversion. All testing is performed by Certified Reference Laboratories and Domestic and International Regulatory Bodies.For more information, contact us now!
0 notes
Text
World Hepatitis Day 2022: Hepatitis is very dangerous, know the symptoms and treatment
World Hepatitis Day 2022: Hepatitis infection increases the risk of many life-threatening diseases. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) report, about 1.1 million people die every year due to hepatitis.
HIGHLIGHTS
World Hepatitis Day is celebrated on 28 July every year, according to the WHO report, about 11 lakh people die every year due to hepatitis.
World Hepatitis Day 2022: There are many such diseases present in our country about which people do not know much. Not knowing the correct information about any disease can prove to be fatal for you. One such disease is hepatitis. World Hepatitis Day is celebrated on 28 July every year and people are made aware. Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver.
Hepatitis infection increases the risk of many life-threatening diseases. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) report, about 1.1 million people die every year due to hepatitis. People of all ages are included in the number of these 11 lakh people.
what is hepatitis infection
Hepatitis is a viral infection. Due to which the liver starts swelling. Due to inflammation, there is a lot of bad effect on the liver. There are many types of hepatitis. But the most common are hepatitis A, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C. If a person is going through any of these three conditions. So the chances of his liver failure or liver cancer are greatly increased. Therefore, it is very important to treat it at the right time.
Major symptoms of hepatitis
Major symptoms of hepatitis
stomach ache
swelling of the body
to vomit
sudden loss of weight
loss of appetite
yellowing under eyes
how to prevent hepatitis
get waxed as soon as possible
get blood screened
stop drinking alcohol
eat healthy diet
Seek doctor's advice in case of discomfort
Weight loss is different for everyone natural no exercise, no dieting faster results click Now
BEST SUPPLEMENT FOR MEN Increase Penis Enhancement click Now
BEST SUPPLEMENT FOR MEN Increase Sex drive click Now
0 notes
Link
Hepatitis is liver inflammation, and the hepatitis B virus leads to hepatitis B. The virus spreads when a person comes in contact with infected blood.
0 notes
Text
Track 3: Hepatitis
Call for Abstracts are open, If you have a paper, poster, workshop, or panel concerning one or more of our topics for this year, submit your abstract before January 31, 2024. At the CME/CPD accredited 14th World Gastroenterology, IBD & Hepatology Conference fro
m December 17-19, 2024, in Holiday Inn Dubai, UAE & Virtual.Submit your abstract/papers here: https://gastroenterology.universeconferences.com/submit-abstract/
WhatsApp us: https://wa.me/442033222718?text=
#Hepatitis#HepatitisAwareness#HepatitisPrevention#HepatitisTreatment#HCV#C#Virus#HBV#B#NoHep#No#LiverHealth#EliminateHepatitis#HepatitisTesting#HepatitisFreeFuture#HepatitisDay#WorldHepatitisDay#HepatitisAdvocacy#HepatitisSupport#GetTested#LiverDisease#HepatitisResearch#EndHepatitis#HepatitisWarrior
0 notes
Text
Determining buffer conditions for downstream processing of VLP-based recombinant hepatitis B surface antigen using multimodal resins in bind-elute and flow-through purification modes.
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) accounts for around 80% of the global burden of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and finally 820,000 deaths annually. Purification of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) from the plasma of the virus carriers was the initial common source of HBV vaccines; however, the inadequate supply of human plasma plus increased risk of viral transmission were the main motives to the production of recombinant HBsAg. Like other virus-like particles (VLPs), rHBsAg has also the potential to be used as vaccine carrier and gene therapy vector.
In the production route of pharmaceutical recombinant proteins, complications of downstream processing (DSP) are yet responsible for the major part of the manufacturing processing cost. Such complications are exacerbated for VLP based proteins as the large size of the particles slows down and even prevents their diffusion through chromatographic resins pores and their access to the large internal surface areas. These issues afflict the resins performance in terms of binding capacity, VLPs recovery and purity
#hepatitis b#hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)#viral transmission#virus-like particles (VLPs)#HBV vaccines#downstream processing (DSP)#hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)#scientific reports
0 notes
Text
Hepatitis B - Symptoms, Treatment, Prevention, and More
Hepatitis B vaccination is important to prevent this serious liver disease. Let us dive deep into the article and learn more about hepatitis B.
0 notes
Text
The Health Risks of the Hepatitis B Virus in Children - A Comprehensive Guide
As parents, it’s important to know the health risks associated with the hepatitis B virus (HBV). HBV can cause serious health complications in children, including liver cirrhosis and death. In this guide, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview of the key health risks of HBV and how you can reduce them. We’ll also cover tips on how to prevent HBV from spreading and how to get appropriate care when it does happen. read more

0 notes
Text
STDs, Sexually Transmitted Diseases, Classification
STDs, Sexually Transmitted Diseases, Classification
STDs can be divided, simply, into two main categories, according to curability. Sexually Transmitted Diseases that can be cured in one category and those that cannot be cured and removed from the body. So, the two main categories are Curable STDs and in curable.
Curable and Incurable STDs
curable Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Curable STDs: These infections can be cured when the patient…

View On WordPress
0 notes
Link
Hepatitis-B-Virus-Nukleinsäure-Nachweis-Kit-Marktbericht wird eine umfassende Analyse der globalen und regionalen Marktgröße und der Marktgröße auf Länderebene, des Segmentierungsmarktanteils und der Segmentgröße, des Marktwettbewerbs, der Verkaufsanalyse, der Auswirkungen regionaler und globaler Marktteilnehmer sowie der Optimierung der Wertschöpfungskette/Lieferkette umfassen , Handelsgesetze, wichtige Unternehmensstrategien, Analysen von Wachstumschancen, Produkteinführungen, Erweiterung des Gebietsmarktes und technologische Innovationen.
0 notes
Text

0 notes
Text
them identify opportunities and potential threats, so they can prepare for the present and future. MRI Research helps organizations to figure out whats happening in a given industry, including demand and supply statistics, degree of competition
0 notes
Text
Physicians have a history of antagonism to the idea that they themselves might present a health risk to their patients. Famously, when Hungarian physician Ignaz Semmelweis originally proposed handwashing as a measure to reduce purpureal fever, he was met with ridicule and ostracized from the profession.
Physicians were also historically reluctant to adopt new practices to protect not only patients but also physicians themselves against infection in the midst of the AIDS epidemic. In 1985, the CDC presented its guidance on workplace transmission, instructing physicians to provide care, “regardless of whether HCWs [health care workers] or patients are known to be infected with HTLV-III/LAV [human T-lymphotropic virus type III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus] or HBV [hepatitis B virus].” These CDC guidelines offered universal precautions, common-sense, nonstigmatizing, standardized methods to reduce infection. Yet, some physicians bristled at the idea that they need to take simple, universal public health steps to prevent transmission, even in cases in which infectivity is unknown, and instead advocated for a medicalized approach: testing or masking only in cases when a patient is known to be infected. Such an individualized medicalized approach fails to meet the public health needs of the moment.
[...]
Masking as a disability accommodation in health care settings should be recognized as part of physicians’ ethical obligations. Access to health care is a particularly fraught issue, as people with disabilities often require more frequent and specialized health care than nondisabled individuals. Physicians have an ethical responsibility to promote the well-being of their patients and do no harm. Wearing a mask on a disabled patient’s request to protect them from contracting COVID-19, which could be deadly for that patient, squarely fits within physicians’ ethical obligation to provide for patients’ care and to ensure their ability to safely partake in health care settings.
92 notes
·
View notes
Text


It did not seem like a good thing when a precious consignment of human tumour samples on its way from Kampala, Uganda, to Heathrow was diverted to Manchester. When the samples finally arrived at the Middlesex hospital in London, they were swimming in murky fluid in their vials as though they had been infected with bacteria.
But when the pathologist Anthony Epstein looked at the fluid under the microscope he saw no bacteria, just individual cells that had been shaken loose from the tumours. And that was just what he needed in order to search for elusive virus particles and test his hunch that they were causing cancer.
In the early 1960s Epstein, who has died aged 102, had heard a lecture by Denis Burkitt, an Irish surgeon working in Kampala, that described strange tumours (now known as Burkitt lymphoma) growing around the jaws of children in equatorial Africa.
Intriguingly, the geographical distribution of the condition seemed to depend on temperature and rainfall, suggesting a biological cause. Epstein, who had been working with viruses that cause cancer in chickens, immediately suspected a virus might be involved, perhaps in association with another tropical disease such as malaria.
Epstein began to collaborate with Burkitt, who supplied him with tumours from children he had treated. But Epstein’s efforts to grow pieces of tumour in the laboratory and isolate a virus had all been unsuccessful until the dissociated cells arrived.
With his graduate student Yvonne Barr, he then decided to look at cultures of these cells in an electron microscope, a powerful instrument that had only recently become available in his lab.
The very first image showed a tell-tale outline that looked like one of the family of herpes viruses. It turned out to be a previously undescribed member of that family, and was given the name Epstein-Barr virus. In 1964, Epstein, Barr and Epstein’s research assistant, Bert Achong, published the first evidence that cancer in humans could be caused by a virus – to be greeted by widespread scepticism even though they went on to demonstrate that EB virus caused tumours in monkeys.
Thanks to samples supplied by Epstein, in 1970 Werner and Gertrude Henle at the Children’s hospital in Philadelphia discovered that EB virus also caused glandular fever. That made it possible to design a test for antibodies to the virus in order to confirm a diagnosis. EB virus turned out to be very common, infecting most children in early life, though it usually causes glandular fever only in older teenagers and young adults. As well as causing Burkitt lymphoma in endemic areas in Africa and Papua New Guinea, it is also associated with a cancer of the nose and throat that is the most common cancer of men in south China, as well as cancers in people whose immune systems have been compromised, such as those infected with HIV.
More recent research suggests that EB virus might also be involved in some cases of multiple sclerosis, and that people who have previously had glandular fever are more susceptible to severe Covid-19.
After the discovery, Epstein and others devoted time and effort to trying to find out under what circumstances EB virus causes cancer. The relationship between the virus, other diseases, human genetics and cancer is complex, and it took decades before the medical community could accept the EB virus as a cause with confidence.
Not until 1997 did the International Agency for Research on Cancer class it as a Group 1 carcinogen, formally acknowledging its role in a variety of cancers.
The discovery of EB virus opened up a whole new field of research into cancer-causing viruses. It also raised the exciting possibility of preventing cancers through vaccination, an advance that has now been achieved in the case of human papilloma virus, which causes cervical cancer, and hepatitis B virus, which causes liver cancer.
By the time of his retirement in 1985, Epstein’s research group at the University of Bristol had developed a candidate vaccine that protected monkeys infected with EB virus against tumours, but neither it nor any other candidate has yet been successfully developed for human use.
Epstein was born in London, one of three children of Olga (nee Oppenheimer) and Mortimer Epstein. Mortimer was a writer and translator who edited The Statesman’s Yearbook for Macmillan from 1924 until his death in 1946. Olga was involved with charitable work in the Jewish community. Anthony attended St Paul’s school in west London, where the biology teacher Sidney Pask encouraged boys to go far beyond the syllabus and whose pupils also included Robert Winston and Jonathan Miller.
Epstein won a place to study medicine at Trinity College, Cambridge. He moved to Middlesex hospital medical school in wartime London to complete his training, before doing his national service in India with the Royal Army Medical Corps. He returned to work at the Middlesex hospital as assistant pathologist, conducting his own research. Thinking electron microscopy might be useful in his studies of cancer-causing viruses in chickens, he spent some time learning the new technique at the Rockefeller Institute in New York (now Rockefeller University). Not long afterwards he attended Burkitt’s lecture and began the serendipitous route to his discovery.
In 1968 he was appointed professor and head of the department of pathology at the University of Bristol, where he remained until his retirement. He moved to Oxford as a fellow of Wolfson College in 1986, becoming an honorary fellow in 2001.
An exemplary scientific good citizen, he served as foreign secretary and vice-president of the Royal Society, and sat on boards and councils for numerous national and international research organisations, including as a special representative of the director general of Unesco; he was also a patron of Humanists UK. Among his many prizes and honorary degrees, he received the international Gairdner award for biomedical research in 1988. He was appointed CBE in 1985 and knighted in 1991.
“It was a series of accidents, really,” he said of his discovery in a conversation with Burkitt they recorded for Oxford Brookes University’s oral history archive in 1991. “Lucky quirks.” Burkitt immediately responded with Louis Pasteur’s aphorism: “Chance favours the prepared mind.”
Epstein was a deeply cultured man who retained a lively interest in many subjects – particularly oriental rugs, Tibet and amphibians – until the end of his life.
He is survived by his partner, Kate Ward, by his children Susan, Simon and Michael, from his marriage to Lisbeth Knight, from whom he was separated in 1965, and who died in 2015, and by two grandchildren and two great-grandchildren.
🔔Michael Anthony Epstein, pathologist, born 18 May 1921; died 6 February 2024
Daily inspiration. Discover more photos at Just for Books…?
11 notes
·
View notes
Text
¿QUE ES EL VPH Y VIH?
VPH
Los virus del papiloma humano (VPH) son un grupo de más de 200 virus relacionados y algunos de estos se transmiten por las relaciones sexuales vaginales, anales u orales. Hay dos grupos de VPH de transmisión sexual: de riesgo bajo y de riesgo alto. Los VPH de riesgo bajo casi no causan enfermedades.
Las infecciones por el VPH por lo general desaparecen por sí solas. Cuando no lo hacen, pueden provocar que crezcan ciertos tipos de cáncer. Estos incluyen: cáncer de cuello uterino en mujeres.
El VPH puede causar cáncer de cuello uterino y otros cánceres, como el de vulva, vagina, pene o ano. También puede causar cáncer en la parte de atrás de la garganta (llamado cáncer orofaríngeo). Esto puede incluir la base de la lengua y las amígdalas.
¿Cuáles son las reacciones del virus del papiloma humano?
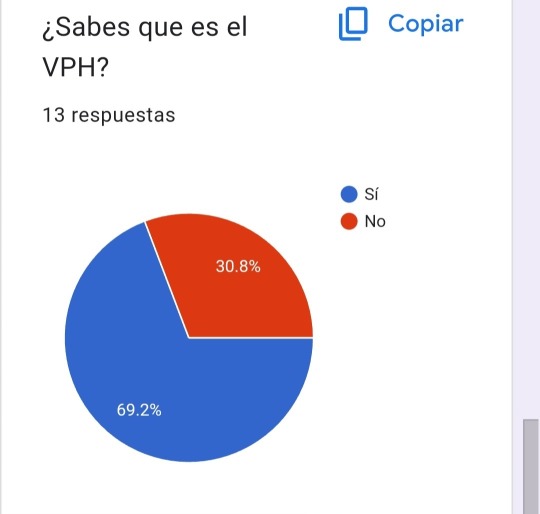
Las mujeres infectadas por el VPH pueden tener verrugas en la vagina, la vulva o el cuello uterino. Los hombres pueden tener verrugas en el pene, el escroto o la ingle. Tanto los hombres como las mujeres pueden tener verrugas genitales en el ano o en los muslos. En la siguiente gráfica que presentaremos se muestra los datos de que porcentaje de las personas sabe que es el VPH:
VIH
El SIDA es causado por el virus del VIH. Este afecta el sistema inmunitario (el encargado de defender tu cuerpo), haciendo que te enfermes más fácilmente. El VIH se transmite durante el sexo, pero los condones ayudan a protegerte.
Síntomas del VIH:
Los síntomas de la infección por el VIH difieren según el estadio en que se encuentre.
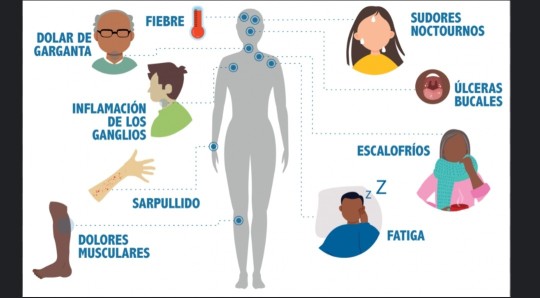
La enfermedad se transmite más fácilmente en los primeros meses posteriores a la infección, pero muchos casos no saben que están infectados hasta las fases más avanzadas. En las primeras semanas posteriores al contagio, algunos casos no manifiestan ningún síntoma, mientras que otros presentan un síndrome gripal con:
fiebre
dolor de cabeza
erupción cutánea
dolor de garganta
A medida que la infección debilita progresivamente el sistema inmunitario, pueden aparecer otros signos y síntomas:
inflamación de los ganglios linfáticos
pérdida de peso
fiebre
diarrea
tos
En ausencia de tratamiento pueden aparecer enfermedades graves:
tuberculosis
meningitis por criptococos
infecciones bacterianas graves
cánceres como los linfomas o el sarcoma de Kaposi
El VIH hace que empeoren otras infecciones, como la hepatitis B, la hepatitis C o la viruela símica.
El VIH se transmite a través del intercambio de líquidos corporales de la persona infectada, como la sangre, la leche materna, el semen o las secreciones vaginales. El VIH también puede transmitirse al bebé durante el embarazo y el parto.
11 notes
·
View notes